19 Best Front End Framework for Web Development
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

Front-end frameworks for responsive web design have become essentially important for the websites. There has already been too much buzz about the ongoing practice of using a responsive framework while initiating web designing. Because of the effectiveness of these frameworks, they are becoming more popular among the developers. Responsive frameworks are far better than the non-responsive ones. Additionally, they are effective and help in the development of user-centric applications.
Responsive web design front-end frameworks include CSS and HTML5 tags and thus they are the best choice to create exceptional website designs. There are several best front-end frameworks available to use to create exceptional websites. Here is a brief on some of the most renowned frameworks used popularly by developers.
1. Twitter Bootstrap
This list would be woefully incomplete without the inclusion of the wildly popular frontend framework, Bootstrap. Created by Twitter developers and initially released in 2011, it's the most used open source framework in the world.
Like any effective frontend framework, Bootstrap includes CSS, HTML and JavaScript, or JS, components. It adheres to responsive web design standards, allowing you to develop responsive sites of all complexities and sizes.
Because it is updated continually, Bootstrap typically includes the latest and best features. For example, it added themes that met Google's material design guidelines shortly after they were published, and it was also upgraded to use Sass as a CSS preprocessor.
Pros:
- Massive community support.
- Widest variety of themes.
- Best browser capability.
- Has both a fluid and fixed pattern grid system.
- More development tools available.
- Many popular websites are built on this framework.
- Superiority in mobile support.
- Most of the celebrated custom web development companies prefer this tool.
Cons:
- Not as lightweight when compared to others. Out-of-the-box file size of 276 KB due to an excessive number of rarely used styles.
- Difficult to use jQuery plugins.
- Websites are easily recognizable.
- The excessive number of HTML classes and DOM elements can be messy and confusing.
Ideal for: Beginners and those who prefer a robust front-end framework.
2. Foundation
Created by web design company Zurb, Foundation is a highly advanced, enterprise-grade frontend framework that is ideal for developing nimble, responsive websites. Used on sites like Facebook, eBay, and Mozilla, it is also fairly complex and may not be suitable for newbies.
This features-rich framework supports GPU acceleration for smooth, lightning fast animations and Fastclick.js for fast rendering on mobile devices. It runs on the Sass preprocessor and includes the Foundation-developed data interchange attribute, which lets you load lightweight HTML sections for mobile and "heavier" HTML sections for larger screens. For a comparison between Foundation and Bootstrap, read our complete article, Bootstrap vs Foundation.
Pros:
- Offers finest of the customization abilities.
- Possess a robust grid system.
- Provides rapid development of code.
- Easy to use templates available for download.
- Offers services for sites as well as emails.
- Design-it-yourself approach.
- Lightweight.
Cons:
- More complex when trying to customize.
- Not a great framework for beginners.
- Less popular in comparison to Bootstrap.
Ideal for:Developers who have decent amounts of experience and who are primarily concerned with developing fast, attractive, responsive websites.
3. Semantic UI
A relative newcomer on the scene, Semantic-UI stands out in several ways and is poised to become one of the most popular front-end frameworks out there.
This framework's main claim to fame is its simplicity. Because it uses natural language, the code is self-explanatory. Even those with very little coding experience will feel fairly at home working with this framework.
Another notable feature of Semantic-UI is that it is integrated with a dizzying array of third-party libraries. So much so, that you probably won't need to use any others. Therefore, the development process is a bit easier and more streamlined.
Pros:
- Semantic class names make for a low barrier of entry, so even beginners can hit the ground running.
- Small file sizes and minimal load times because you can load only the components that you need; each has its own JS file and style sheet.
- Versatile elements make for easy customization.
Cons:
- Very large packages when compared to Foundation and Bootstrap.
- Those with more complex design and development needs may find this framework lacking.
Ideal for: Beginners and those who want a lightweight, nimble framework.
4. Material UI
If you're looking for a front-end framework that makes it easy to adhere to Google's material design guidelines, you can't go wrong with Material UI. It is by far the most elaborate framework to implement these guidelines thus far, but there is one caveat: It isn't meant to be a starting point for a brand-new web design project.
Loaded with ready-to-use CSS and material design-compliant components, Material UI uses a CSS-in-JS solution. This unlocks many great features including theme nesting, dynamic styles, self-support, etc.
Pros:
- The easiest way to meet Google's material design guidelines when using a framework.
- Highly customizable.
Cons:
- Not intended to serve as a starting point for from-scratch web design projects.
- Need a decent understanding of React to use effectively.
Ideal for: Developers who understand and have experience with React and who need an easy way to adhere to material design guidelines.
5. Materialize
The Materialize responsive front-end development framework also implements Google's material design specifications and is loaded with ready-to-use buttons, icons, cards, forms, and other components. It is offered in both a standard version and in one that runs on Sass.
Materialize includes a convenient IZ column grid feature that can be used for website layouts. It is also loaded with CSS that's ready to use out of the box for material design shadows, typography, colors, and other features.
Additional features include ripple-effect animation, drag-out mobile menus, Sass mixins, and more.
Pros:
- Huge selection of components.
- Responsive support ensures that websites are supported across all devices.
Cons:
- The large file size makes this a bulky framework to work with.
- No support for Flexbox model.
Ideal for: Less experienced developers who need guidance regarding Google's material design specifications.
6. UIKit
UIKit is a highly modular front-end framework that stands out among most front-end development frameworks for many reasons. Chief among them is the fact that it includes both Less and Sass CSS preprocessors.
Loaded with an array of nimble, responsive components with consistent naming conventions, UIKit has become one of the most popular front-end frameworks out there.
It's more than 30 extendable, modular components can be combined for even more versatility. It includes navigation components like side navigation bars; elements like HTML forms and tables; JavaScript components like off-canvas bars and modal dialogs; common elements like buttons, badges, and overlays; and layout components, including a fluid, completely responsive grid system.
Pros:
- Highly customizable.
- Exceptionally modular, so you can add components to the style sheet without negatively impacting overall style.
- Create advanced user interfaces using components like nestable.
Cons:
- Very few resources out there due to the relative newness.
Ideal for: Fairly experienced developers due to the current lack of available resources. Otherwise, it is great for simple and complex projects alike.
7. Pure
Created by the Yahoo development team, Pure comes with a lightweight array of CSS modules that can be used in just about any project. Using Pure, you can easily create responsive buttons, menus, grids, tables, and other features. Because it is purely CSS based, however, it does not support JavaScript or jQuery plugins.
When minified and compressed with Gzip, Pure clocks in at just 4.5 KB, making it one of the lightest and nimblest front-end development frameworks out there. As a result, it is terrific for mobile website development, and many developers rely on it for precisely that.
Pros:
- Extremely lightweight, ensuring fast loading times even on mobile devices.
- A flexible array of CSS modules can be used on just about any web design and development project.
Cons:
- CSS only - does not include jQuery or JS plugins.
Ideal for: Developers who are focusing on creating responsive, fast mobile websites.
8. CreateJS
CreateJS is a suite of open-source JavaScript libraries and tools for creating rich, interactive HTML5 content. It consists of 5 modular JavaScript libraries. It will help you with implementing animation effects, supporting HTML5 audio on your website, and much more.
Adobe, Microsoft, and AOL sponsor this project.
Pros:
- It is helpful for rich, interactive HTML5 content.
Cons:
- You have basic knowledge of JavaScrip.
Ideal for: It is ideal for creating animation effects and HTML5 Audios on your website.
9. HTML5 Boilerplate
In 2010, HTML5 Boilerplate became one of the first, and subsequently, most popular open-source front-end web development tools for getting HTML5 websites and web apps up and running in no time. It’s a compilation web development solution that enables our websites to support modern web browsers.
Included in HTML5 Boilerplate is a mobile-friendly HTML template, placeholder icons, CSS resets for normalizing/standardizing your stylesheet property values, standard media queries for popular viewing screens, an HTML5shiv for non-modern web browsers, and more.
Pros:
- It is an open-source front-end web development tool.
- Mobile-friendly HTML template.
Cons:
- It required basic knowledge of HTML/HTML5 and CSS/CSS3.
Ideal for: It is ideal for designing responsive websites.
10. Milligram
Milligram is another extremely lightweight framework similar to Skeleton. When Gzipped, it comes out to just 2 KB in size and is used to provide developers with a simplistic and convenient starting point.
Milligram’s grid system is different than most because of its use of the CSS Flexible Box Layout Module standard. It also includes a few key components for getting you started including typography, buttons, forms, lists, tables, blockquotes, etc.
Pros:
- Very lightweight, only 2 KB when Gzipped.
- Uses CSS Flexbox as the grid system.
Cons:
- Few resources available due to the relative newness.
- Minimal styling components available compared to other larger frameworks.
Ideal for: Developers who are creating a small project that doesn't require any styling components and want to use a CSS Flexbox grid system.
11. Susy
Some would argue that Susy isn't a Front-end Framework in the truest sense of the term because it is focused on solving complex layout needs. Many classify Susy as a grid maker more than anything, but it can be an indispensable tool for those who have specialized layout needs.
Susy arms you with mixins that can be used to create grids. The framework does all of the calculations for you, saving a lot of time and effort.
With Susy, you can create any kind of grid layout imaginable. If you have been looking for a way to do this, Susy may be the answer.
Pros:
- Superior flexibility, so you can create any kind of grid layout that you need.
- Automatically performs all calculations.
Cons:
- Does not cover all aspects of website design, so you still need another framework solution.
- No pre-built grids.
Ideal for: Anyone who has unique or specialized layout requirements.
12. Zebra
Zebra is a rich UI open-source framework that leverages HTML5 canvas as the backbone of its rendering abilities.
Zebra says that using it “isn’t rocket science” and that you can get started in 5 minutes.
13. Siimple
Flexible, aesthetically built and a concise front-end CSS framework to accomplish clean web pages. Siimple is beautiful and mostly used for building web pages that are flat and clean. Working on these simple things sometimes proves to be exceptionally well for the development of user-centric websites. This framework is certainly minimal, having a few lines of codes that can also be zipped down to 6KB in total size. This framework is suitable for newbies who are just starting with their website designing and require a framework to experiment freely. Siimple helps such developers to create minimal and clean web designs.
14. Less Framework
Less Framework is a modern Front-end framework for building responsive designs. Similar to Skeleton (discussed above), Less Framework focuses on being just a plain and simple layout grid framework.
It has 4 pre-built layouts: Default, Tablet, Mobile, and Wide Mobile.
15. Montage HTML5 Framework
Being an HTML5 framework, Montage is great to kick start modern web page development. Montage has got the elements that help in the creation of scalable and feature-rich websites. These exceptional elements also help to maintain the HTML5 applications for a range of devices whether a desktop or a smartphone. Montage is amazing in its ways. It has got reusable components along with HTML templates in addition to the declarative component model, declarative data binding, and much more than it.
16. SproutCore
SproutCore is a front-end framework for building HTML5 apps rapidly.
It follows the MVC architecture pattern and promises its users the ability to craft native-like user experiences for the Web.
17. Cascade
Cascade is a great relief to the developers as it offers both semantic and non-semantic grid layouts along with base templates, navigational elements, table designs. Cascade has got a universal approach and thus it is easy for designers to include several elements in their design. With Cascade in use, designers, as well as developers, have got the option of creating high-performance web pages for a variety of browsers right from the older ones to the new browsers. Cascade can be used by developers to choose and work on the components most important for a particular project.
18. Skeleton
Skeleton is a lightweight responsive boilerplate that contains only 400 lines of code. This framework is meant to include only the minimum requirements to get you started on the development of a web project. It is not meant to be all-inclusive such as other frameworks as mentioned above.
Skeleton is also responsive, based on a 12-column grid system, and includes the bare essentials such as buttons, lists, tables, forms, etc.
Pros:
- Extremely lightweight.
- Greater simplicity and useful for smaller projects.
Cons:
- It does not include a wide selection of utility/styling components such as larger frameworks do.
Ideal for:Someone who is creating a smaller project that doesn't require all of the style components of a larger framework.
19. HTML KickStart
One of the newest kids on the block, HTML5 KickStart is a lean and mean package of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files that promises to save UI developers hours of work.
At about 300KB, HTML KickStart packs quite a punch: UI components like stylish buttons and navigation bars, scalable icons (using Font Awesome), a responsive grid layout, a touch-enabled slideshow component and so on.
FAQs - Front-end frameworks
1. Which is the Best CSS Framework?
Answer : That depends on the website you’re looking to build. The most popular CSS framework, however, is Bootstrap.
2. What is a CSS Framework?
Answer : A CSS framework is a library of CSS stylesheets with pre-done code to help you design websites faster.
3. Why Do CSS Frameworks Use Preprocessors?
Answer : CSS frameworks use preprocessors to automate tasks.
4. Which Files Do You Need for CSS Frameworks?
Answer : You need CSS files from respective frameworks and sometimes JavaScript and HTML files.
Conclusion
There are plenty of Front-end frameworks, but we have chosen the best Front-end frameworks that matter in 2023. Out of these 19, we cannot say which one is best, as each has its own set of features. By choosing the right Front-end frameworks for your needs, all the complicated and time-consuming styling is taken care of, and you can focus on writing business logic.
If you’re just starting out with CSS and UI, go for Pure, or Skeleton. However, to build more complex elements, you’ll need a more inclusive framework like Bootstrap, Foundation, Material UI etc. read our complete article, Bootstrap vs Foundation.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Bootstrap Front End Framework for Web Design
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
Bootstrap is a free and open-source CSS framework directed at responsive, mobile-first front-end web development. It contains CSS- and (optionally) JavaScript-based design templates for typography, forms, buttons, navigation, and other interface components.
Highlights:
- Author: Mark Otto, Jacob Thornton
- Developer's: Bootstrap Core Team
- Initial release: August 19, 2011
- Written in: HTML, CSS, Less (v3), Sass (v4) and JavaScript
- Platform: Web platform
- Open-source: Yes
- Website: https://getbootstrap.com
- Alexa Rank: 2,108
Bootstrap 4 Alpha 6 Features:
1. Rewritten grid system in flexbox: They improved the grid system with three major changes. Here, one can disable the grid classes by the SASS variable. You can add a grid customization section to the documents. You will see also witness simplified grid classes. These changes are available in both standard and flexbox grids.
2. Flexbox by default: Along with flexbox being the default system. There are flexbox grids, also available, apart from standard ones. And new flexbox alignment utility classes at hand for distributing items as well.
3. IE9 support: Bootstrap CSS has released this long-awaited update of IE9 support.
4. Forms: With development to Alpha 4, there are significant changes in forms. There are necessary improvements in sizing, alignment, and component layout. The ‘fresh form validation and help text options are ready. And the documentation for forms is simplified too.
5. Automatic equal-width grid columns: Breakpoint-specific column classes can be employed for columns with equal width.
6. Updated and improved Navbar: Earlier there were certain styles for nav components that could not be set by variables. This update takes care of that and also adds some new features to it.
7. Auto margins for easy spacing: They improved the auto margins for easy spacing.
8. Change in system fonts: Helvetica/Arial font was old system fonts. They are replaced with a system font stack of modern, and strong fonts. This is done for companies like Apple, Google, Mac, to target the latest devices. Although, there is no such update available for Linux users.
Pros:
- Massive community support.
- Widest variety of themes.
- Best browser capability.
- Has both a fluid and fixed pattern grid system.
- More development tools available.
- Many popular websites are built on this framework.
- Superiority in mobile support.
- Most of the celebrated custom web development companies prefer this tool.
Cons:
- Not as lightweight when compared to others. Out-of-the-box file size of 276 KB due to an excessive number of rarely used styles.
- Difficult to use jQuery plugins.
- Websites are easily recognizable.
- The excessive number of HTML classes and DOM elements can be messy and confusing
Popular Brands Using Bootstrap:
- Lyft
- Vogue
- Riot Design
- Newsweek
Ideal for: Beginners and those who prefer a robust front-end framework.
Bootstrap Alternatives: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
Bootstrap Alternatives: If you want to explore bootstrap alternatives. Visit Here
Bootstrap, originally named Twitter Blueprint, was developed by Mark Otto and Jacob Thornton at Twitter as a framework to encourage consistency across internal tools. Before Bootstrap, various libraries were used for interface development, which led to inconsistencies and a high maintenance burden.
After a few months of development by a small group, many developers at Twitter began to contribute to the project as a part of Hack Week, a hackathon-style week for the Twitter development team. It was renamed from Twitter Blueprint to Bootstrap and released as an open-source project on August 19, 2011. It has continued to be maintained by Mark Otto, Jacob Thornton, and a small group of core developers, as well as a large community of contributors.
Bootstrap 2
On January 31, 2012, Bootstrap 2 was released, which added built-in support for Glyphicons, several new components, as well as changes to many of the existing components. This version supports responsive web design, meaning the layout of web pages adjusts dynamically, taking into account the characteristics of the device used (whether desktop, tablet, or mobile phone).
Bootstrap 3
The next major version, Bootstrap 3, was released on August 19, 2013. It redesigned components to use flat design and a mobile-first approach.
Bootstrap 4
Mark Otto announced Bootstrap 4 on October 29, 2014. The first alpha version of Bootstrap 4 was released on August 19, 2015. The first beta version was released on 10 August 2017. Mark suspended work on Bootstrap 3 on September 6, 2016, to free up time to work on Bootstrap 4. Bootstrap 4 was finalized on January 18, 2018.
Significant changes include:
- Major rewrite of the code.
- Replacing Less with Sass.
- Addition of Reboot, a collection of element-specific CSS changes in a single file, based on Normalize.
- Dropping support for IE8, IE9,[contradictory] and iOS 6.
- CSS Flexible Box support.
- Adding navigation customization options.
- Adding responsive spacing and sizing utilities.
- Switching from the pixels unit in CSS to root ems.
- Increasing global font size from 14px to 16px.
- Dropping the panel, thumbnail, pager, and well components.
- Dropping the Glyphicons icon font.
- Huge number[quantify] of utility classes.
- Improved form styling, buttons, drop-down menus, media objects, and image classes.
- Bootstrap 4 supports the latest versions of Google Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, Opera, and Safari (except on Windows). It additionally supports back to IE9 [contradictory] and the latest Firefox Extended Support Release (ESR).
Bootstrap 5
Bootstrap 5 is a updated version of bootstrap4 and Bootstrap 5 alpha was officially released on June 16, 2020 after several months of refining. With all of the major changes in this version, the Boostrap 5 development team informed the users that the current version is still in alpha version thus, breaking changes will continue to occur until the first beta is released so it’s better to always check the open issues and pull requests on their official GitHub repository for open questions and feedback.
Summary of the most important changes:
- jQuery was removed
- Switch to Vanilla JavaScript
- Drop Internet Explorer 10 and 11 support
- Improved grid system
- Improved documentation
- Improved modularity
- Improved forms
- New responsive font
- New utilities & helpers
- Easier customization & theming
- Lighter package
- New API available
Bootstrap Alternatives: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Foundation Front-End Frameworks for Web Deisgn
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
Foundation is a CSS framework designed by ZURB in September 2011. It has a slightly more advanced interface compared to other frameworks. Foundation is compatible on multiple browsers and hand held devices. The responsive menu is one of its greatest assets. The menu is incredible when it comes to functionality and can also be easily styled using CSS. This responsive framework allows designers and developers to create elegant websites with more of a design-it-yourself approach. It has responsive grid ( HTML & CSS) UI components, templates, and code snippets, including typography, forms, buttons, navigation and other interface elements, as well as optional functionality provided by JavaScript extensions.
Highlights
- Developer's: ZURB
- Initial release: September 2011
- Written in: HTML, CSS, Sass and JavaScript
- Open source: Yes
- Website: get.foundation
- Alexa Rank: 36,606
Foundation 6.4 Features:
1. Includes XY grids: The latest version of Foundation includes a strong default grid system namely XY grids. This makes you control the layouts displayed both horizontally and vertically.
2. Flexbox by default: Although there is a feature available which allows the fall back to float-mode, Flexbox is what they recommend.
3. Smooth scrolling: This feature can be used to create “smooth scroll” behavior for any link available inside the page.
4. Shifted to ES2016 JavaScript: Foundation moved its javascript architecture to ES2016 module-based architecture. If one does not have a module bundler. The drop-in compiled JS files in dist/js will provide backward compatibility.
5. Easier prototyping: The process of prototyping and production often confuses people. With this feature, Foundation offers a better way and a “prototype mode” to speed up the prototyping function.
Pros:
- Offers finest of the customization abilities.
- Possess a robust grid system.
- Provides rapid development of code.
- Easy to use templates available for download.
- Offers services for sites as well as emails.
- Design-it-yourself approach.
- Lightweight.
Cons:
- More complex when trying to customize.
- Not a great framework for beginners.
- Less popular in comparison to Bootstrap.
Popular brands using Foundation
- Adobe
- Amazon
- Ebay
- Pixar Projection
- Washington Post
- Herschel Supply
Ideal for: Developers who have decent amounts of experience and who are primarily concerned with developing fast, attractive, responsive websites.
Foundation Alternatives: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
Foundation emerged as a ZURB project to develop front-end code faster and better. In October 2011, ZURB released Foundation 2.0 as open source under the MIT License. ZURB released Foundation 3.0 in June 2012, 4.0 in February 2013, 5.0 in November 2013, and 6.0 in November 2015. The team started working on the next version of Foundation for Sites 7 which most likely will drop support for older browsers and implement newer technologies like flexbox or maybe calculated grid system.
Foundation for Emails, formerly known as ZURB Ink, was released in September 2013.
Foundation for Apps was released in December 2014.
Foundation was designed for and tested on numerous browsers and devices. It is a mobile first responsive framework built with Sass/SCSS giving designers best practices for rapid development. The framework includes most common patterns needed to rapidly prototype a responsive site. Through the use of Sass mixins, Foundation components are easily styled and simple to extend.
Since version 2.0 it also supports responsive design.This means the graphic design of web pages adjusts dynamically, taking into account the characteristics of the device used (PC, tablet, mobile phone). Additionally, since 4.0 it has taken a mobile-first approach, designing and developing for mobile devices first, and enhancing the web pages and applications for larger screens.
Foundation is open source and available on GitHub. Developers are encouraged to participate in the project and make their own contributions to the platform.
1. Grid system and responsive design: Foundation comes standard with a 940 pixel wide, flexible grid layout. The toolkit is fully responsive to make use of different resolutions and types of devices: mobile phones, portrait and landscape format, tablets and PCs with a low and high resolution (widescreen). This adjusts the width of the columns automatically.
2. Understanding CSS stylesheet : Foundation provides a set of stylesheets that provide basic style definitions for all key HTML components. These provide a browser and system-wide uniform, modern appearance for formatting text, tables and form elements.
3. Reusable components : In addition to the regular HTML elements, Foundation contains other commonly used interface elements. These include buttons with advanced features (for example, grouping of buttons or buttons with drop-down option, make and navigation lists, horizontal and vertical tabs, navigation, breadcrumb navigation, pagination, etc.), labels, advanced typographic capabilities, and formatting for messages such as warnings.
4. JavaScript components and plug-ins : The JavaScript components of Foundation 4 were moved from jQuery Javascript library to Zepto, on a presumption that the physically smaller, but API-compatible alternative to JQuery would prove faster for the user. However, Foundation 5 moved back to the newer release JQuery-2. "jQuery 2.x has the same API as jQuery 1.x, but does not support Internet Explorer 6, 7, or 8." The official Zurb blog explains, and the unsigned writer claims that the switch back was due to issues of compatibility with customized efforts; and that performance was found to be not as good, on use testing with the newer jQuery-2.
Foundation jQuery components provide general user-interface elements and branded extensions. The list includes dialog, tooltips, carousels, alerts, clearing, cookies, dropdown, forms, joyride, magellan, orbit, placeholder, reveal, section, topbar, flex video, and many others. Additional jQuery plug-ins can be installed into the Foundation framework to provide advanced functionality in any UI area, including animation and "off-canvas" elements like slide-in menus.
Foundation Alternatives: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Comparison Bootstrap Between Foundation
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

When it comes to being a developer and designer you usually always reach a crossroads of which CSS framework should you use? There are so many Front-end frameworks, but two of the most commonly mentioned ones are Bootstrap and Foundation.
Here is a comparison between Bootstrap and Foundation:
| Parameters | Bootstrap | Foundation |
|---|---|---|
| Current Version | V 4.0 alpha 6 | V 6.4 |
| Preprocessors | Less & Sass | Sass |
| Grid system | Flexbox-based | Floated (flexbox in latest version) |
| Customization | Basic GUI customizer | Basic GUI customizer |
| Community | 112k + (stars on Github) | 25.8k + (stars on Github) |
| Browser support | Chrome (Mac, Windows, iOS, and Android), Safari (Mac and iOS only), Firefox (Mac and Windows), Opera (Mac and Windows) IE9+ | Chrome (Mac, Windows, iOS, and Android), Safari (Mac and iOS only), Firefox (Mac and Windows), Opera (Mac and Windows), IE9+ |
| Design | Customizable; a variety of designs. | Not that appealing |
| Normalization/ Reset | reboot.css | normalize.css |
| Inline forms | Yes | No |
| License | MIT | MIT |
| Website | getbootstrap.com | get.foundation |
Front-end Frameworks List: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
Conclusion: In order to make a conclusion which framework is better, you have to decide which one suits your requirements. In order to decide you must go through the features that each has to offer. With the given features currently listed, you must overlook that Foundation is quickly evolving and new updates are released frequently. Simply put, Foundation offers a slightly more complex, but a do it yourself style approach that will create something more unique and custom. Whereas Bootstrap allows for easy creation of simple yet elegant websites, with very little knowledge of CSS and JavaScript. Any CSS framework you chose will drastically simplify the web development process and provide the necessary foundations to build an amazing website.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
What is the best CSS Framework
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

When it comes to being a developer and designer you usually always reach a crossroads of which CSS framework should you use? There are many out there to choose from, but two of the most commonly mentioned ones are Bootstrap and Foundation. In this post, we will be comparing the two CSS frameworks, Bootstrap vs Foundation. Read more below about how using a framework can help speed up and streamline your development and design process.
What is a CSS framework?
Building a website or app from scratch can take a lot of time and development. A CSS framework is commonly used by developers and designers as a tool to speed up the process. A CSS framework, also sometimes referred to as a frontend framework, is essentially a package that is made up of predefined HTML, CSS, and JS which can be used when starting to build out a project. This way you don't have to code from a blank slate every time you need to create a website or web application. In this post, we are specifically focusing on frontend frameworks which usually have to deal with what the visitor actually sees.
A CSS framework usually consists of the following components:
- HTML code which helps make up the structure of the pages.
- Typography styles.
- CSS to visually change how elements appear (a standard set of easy to use classes).
- JavaScript to change dynamic elements such as drop downs, expanding menus, etc.
- Responsive media queries.
- Cross-browser compatibility fixes.
Front-end Frameworks List: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Front-End Frameworks
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
As developers, we often find ourselves looking for ways to be more efficient. For many of us, this means turning to front-end frameworks. Whether it is robust, full-featured frameworks like Bootstrap or Foundation or more foundational frameworks such as Skeleton or Pure, developers are turning to these tools to get a jumpstart on web projects.
Advantages of Using a Front-end Framework
First, let’s take a look at a few Advantages of using a front-end framework.
- Easy and quick to get started.
- They are great for prototyping.
- You can gain momentum by “getting something on the page”.
- They are handy when you are against tight deadlines.
- They provide a solid foundation for responsive design.
- Components of the UI have a base style to be extended (forms, buttons, navbar, etc.)
- The base styles persist throughout.
- They provide a consistent UI design for developers who lack design skills, which is great for things like intranet sites or documentation.
- They provide a base development for non-developers to get something up quick for prototyping or mockups.
Good looking UI, even out-of-the-box
- Components of the UI have a base style to be extended (forms, buttons, menus, etc.)
- The base styles persist throughout.
- They provide a consistent UI design for developers who lack design skills, which is great for things like intranet sites or documentation.
- They provide a base development for non-developers to get something up quick for prototyping or mockups.
Code is reliable and tested
- Code is widely used, especially open source.
- Cross-browser compatibility is built-in, so you know where it will work.
Help is readily available
- Front-end frameworks are widely used, so answers to common problems are easy to find.
- The documentation is usually thorough.
- Free and professional themes and templates may be available.
Disadvantages of Using a Front-end Framework
While development frameworks have been gaining in popularity over the past few years, not all frameworks are created equal and often a front-end framework is not the right tool for the job. Here are a few disadvantages I have found to using them:
They can be too opinionated
Although they are easy to get started, they can require more time down the road to add features and customizations. You might find yourself fighting the base styles with overrides (wasting all that precious time you saved) to get the desired results. This can also lead you to write code that does not evolve gracefully as the project needs change.
Note: Some of these risks can be mitigated by selecting a framework which is more flexible or closely resembles your project. I would advise testing out different frameworks, so you have a better understanding of the advantages and limitations of these tools when a new project comes along.
You’re not learning how to code
It is easy to fall into the trap of only learning the framework and not learning how to develop. You often miss out on valuable experience with the underlying technology. If you are not already an expert, it is important to understand the code which powers the framework. This knowledge will make life a lot easier when you run into complex challenges and will make you a better developer overall.
Updates can introduce issues
- Updating may introduce conflicts with your code.
- When it comes to updates, at the mercy of the framework developers. Sure, you can choose not to update, but you then risk falling behind.
Technical debt
- Developers coming onto the project will need to understand the framework in order to contribute.
- “One-size-fits-all” frameworks tend to have a larger footprint and can add unnecessary bloat to your project.
Front-end Frameworks List: If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
Conclusion: As with most development decisions, the choice to use a framework and which framework to use should be made based on the requirements of a specific project. What may be perfect for a small marketing website, may not be so great for building a highly-customized web portal. With new frameworks popping up frequently, but as developers, it’s still important to be diligent in selecting frameworks that suit our needs and the needs of our clients.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
How to Build a Responsive Website from Scratch
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
You can create custom responsive designs using just HTML and CSS only. Some of the great responsive email templates are designed in using just HTML and CSS because most of the email clients do not support Media Queries.
But you can’t make a complex custom responsive design by using HTML and CSS, for that purpose you need to use Media Queries and sometimes, even javascript
Today, a website must not look good only on a desktop screen, but also on tablets and smart phones.
A website is responsive if it can adapt to the screen of the client.
Responsive web design is extremely important nowadays and is one technique you need to master as a web designer.
In this article, I’ll show you how to easily build a custom responsive website and how to apply custom responsive design techniques on existing web pages in three easy steps.
Before you start a responsive design from scratch you need to keep some points in your mind as below:
1. Use meta tag in your website top of the header:
Viewpoint Meta Tag: Put viewport meta tag inside your page head area. This viewport tag will prevent the browser from zooming out the page. Thus it will remain the same width of the screen size.
Example:
2. Every code should be in % (percentage) instead of px (pixels).
Example:
3. Try to use flexbox layout as much as possible.
The Flexible Box Layout Module makes it easier to design a flexible responsive layout structure without using float or positioning.
Before the flexbox layout module, there were four layout modes:
- Block, for sections in a webpage.
- Inline, for text.
- Table, for two-dimensional table data.
- Positioned, for the explicit position of an element.
Example:
4. Beautify your design for tablets and smart phones screen by using media queries.
Now apply media queries in our CSS file, this is done with the help of condition statements. In the condition provide the min-width and max-width to target screen size.
Conclusion:
Hope you like this Responsive Website from scratch (HTML & CSS). I would also like to tell you that designing a responsive website from scratch can be a time-consuming job. There is also an easy alternative for responsive web design.
Alternatives of Responsive Web Design:
If you want to explore more responsive Front-end Frameworks for your upcoming projects than you can Visit Here.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Adobe Dreamweaver HTML Editor
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

Adobe Dreamweaver is a proprietary web development tool from Adobe Inc. It was created by Macromedia in 1997 and developed by them until Macromedia was acquired by Adobe Systems in 2005.
Adobe Dreamweaver is available for the macOS and Windows operating systems.
Following Adobe's acquisition of the Macromedia product suite, releases of Dreamweaver subsequent to version 8.0 have been more compliant with W3C standards. Recent versions have improved support for Web technologies such as CSS, JavaScript, and various server-side scripting languages and frameworks including ASP (ASP JavaScript, ASP VBScript, ASP.NET C#, ASP.NET VB), ColdFusion, Scriptlet, and PHP.
Highlights:
- Developer(s) - Adobe Inc. (2005–present)
- Macromedia - (before 2005)
- Initial release - December 1997; 22 years ago
- Stable release - 2020 (20.1) / February 2020; 5 months ago
- Written in - C++
- Operating system - Windows 10 version 1703 and above, macOS 10.12 Sierra and above
- Type - HTML editor, programming tool, integrated development environment (IDE)
- License - Trialware software as a service
- Website - https://www.adobe.com/products/dreamweaver.html
Key Features:
1. Fast, flexible coding: Create, code, and manage dynamic websites easily with a smart, simplified coding engine. Access code hints to quickly learn and edit HTML, CSS, and other web standards. And use visual aids to reduce errors and speed up site development.
2. Set up to site up in fewer steps: Get your sites up and running faster with starter templates that you can customize to build HTML emails, About pages, blogs, e-commerce pages, newsletters, and portfolios. And because Dreamweaver is part of Creative Cloud, you can quickly bring in assets from your Libraries and Adobe Stock to enhance your sites.
3. Dynamic display on every device: Build responsive websites that adapt to fit any screen size. Preview your sites and edits in real time to make sure your pages look and work the way you want before you publish.
4. Seamless Live View editing: Edit text and image properties and add classes directly in Live View with one click — then preview changes instantly. No need to switch to a separate edit mode.
5. Multi-monitor support for Windows: Now you can expand your workspace by displaying your pages on multiple monitors.
6. Redesigned, modern UI: A streamlined and clutter-free interface lets you customize your workspace to show only the tools you need to code.
7. Git support: Collaboration is easy with Git support. Manage all your source code within Dreamweaver and perform all common operations right from the Git panel.
Alternatives to Adobe Dreamweaver
- Visual Studio Code HTML Editor
- Notepad++ HTML Editor
- Bubble WYSIWYG Editor
- Sublime Text HTML Editor
- Atom HTML Editor
- CKEditor WYSIWYG Editor
- TinyMCE WYSIWYG Editor
- NetBeans HTML Editor
- Komodo Edit HTML Editor
- Froala WYSIWYG Editor
- Brackets HTML Editor
- CoffeeCup HTML Editor
- Editor.js WYSIWYG Editor
- Phase 5 HTML Editor
- Kompozer WYSIWYG Editor
- UltraEdit HTML Editor
- BareBones Edit HTML Editor
- TextMate HTML Editor
- Setka WYSIWYG Editor
- Aptana Studio HTML Editor
- CotEditor HTML Editor
- Bluefish HTML Editor
- NoteTab HTML Editor
If you want to explore more about Text Editor or WYSIWYG Editor, We recommend you to go through our detailed article of HTML Editors.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
What is Reseller Hosting? And How Does It Work?
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

Reseller web hosting is an option that involves one company (a hosting provider) renting hard drive space and bandwidth to another company (small-midsize business), who then rents the space to third parties (entrepreneurs-small business). Simply put, reseller hosting is the ability to provide hosting to your own clients as if you yourself were the web hosting company.
This is typical for aspiring entrepreneurs who want to start their own web hosting firm or for current web developers and designers who desire to add additional services to their brand.
Advantages of Reseller Hosting
1. Cost : Plans for reseller hosting are fairly cheap. This is why they’re a good option for people looking to get into the web hosting business. Additionally, it simplifies things because you don’t have to purchase the technology, infrastructure, and equipment usually needed to become a web hosting service provider.
2. Focus on the Business : When you choose reseller hosting you can focus on the business aspects rather than the technical aspects of running a web hosting business. This is because all of the tasks related to updates, server maintenance, connectivity, security and so forth, are the responsibility of the web hosting service you’ve rented or purchased from.
3. Room to Expand : If you have a website that gets a lot of traffic, has a lot of pages or your business has several sites, reseller hosting will provide you with a larger number of features and space. For instance, you can run different parts of your sites from different URLs and different servers without having to purchase additional hosting plans.
4. Additional Features : In comparison to basic hosting plans, reseller hosting has a greater number of features. The control panel for the website will also be more powerful, enabling you to manage your site more effectively. Furthermore, a lot of companies will offer unlimited SSL certificates as well as features such as Cpanel.
5. Build Your Brand : Although you’re selling the resources of another web hosting service provider, reseller hosting lets you build your own identity and brand. Essentially, this means that clients won’t know that you’re renting from another web hosting company.
6. Income Opportunities : It’s possible to make additional profit from reseller hosting by selling add-ons such as SSL Certificates, Dedicated Hosting, VPS Hosting, Dedicated IP, domain name registrations, etc.
Disadvantages of Reseller Hosting
1. You’re Dependent on the Original Web Hosting Company : The quality of the original web hosting company will determine the success of your business. This means that if their server regularly goes down or if there are a lot of technical issues, your business will be affected.
2. You’ll Need to Dedicate Time to Customer Service : If you’re providing a web hosting service, even if it's reseller hosting, you’re still responsible for answering questions from clients. If you don’t take the time to answer these questions correctly, it could ruin your business.
3. High Level of Difficulty : Unless you’re an expert at running a website you’re going to find the features and control panels of reseller hosting difficult.
4. Changing Providers will Affect Your Clients : If you decide to change your web hosting provider you have to shift all the data from your clients. This can be incredibly difficult so it’s recommended that you have a dedicated server or Virtual Private Server (VPS). Having a dedicated server or VPS will make it easier to change providers but it does make things more expensive.
5. Limited Access to the Server : You are going to have to go through your web hosting service provider for most things because reseller hosting only offers limited access to the server.
How Do You Make Money as a Reseller?
Nobody is going to pretend you’re going to get rich with reseller hosting but you can make extra income from it. You also gain an income from those clients attracted by the complete packages a web designer can offer that includes site setup and hosting in one.
Essentially, if you offer full managed hosting to your customers, you can charge a premium as compared to standard hosting, where you would charge let’s say $50/month to each client, but handle all their technical needs and maintenance, such as upgrades of core CMS, plugins, backups, security, etc.
Your residential income depends on the wholesale price you pay to the host and the maximum your market can sustain. As mentioned, some hosts charge a monthly maintenance fee for reseller hosting accounts but many don’t. It pays to research the market, what’s on offer and at what price before you settle on one provider.
Most reseller accounts are scalable so you can start small when you first launch your offering and scale up only when you need to. This is a cost-effective way to do business and keeps your costs down as much as possible.
How to Choose the Best Reseller Hosting?
If you have your business plan in order then the main task left to you is to choose the best reseller hosting for your needs. When you’re considering a web hosting service that has reseller plans make sure to check for the following:
- Does the reseller have a solid reputation for reseller hosting?
- Does the hosting service have a plan that meets your budget and hosting needs?
- Do they have a good software interface to manage your reseller account?
- If you’re not satisfied, do they have a money-back guarantee?
- Do you have access to technical support? What kinds of support services? Phone/email/chat?
- If your business grows and requires an upgrade, will they provide an upgrade path for your hosting service?
Choosing a service is often a matter of personal preference and perspective, but this checklist should help lead you to a reseller host that will provide the solution you need.
FAQs - Reseller Hosting
1. What is reseller hosting?
Answer :Reseller web hosting is an option that involves one company (a hosting provider) renting hard drive space and bandwidth to another company (small-midsize business), who then rents the space to third parties (entrepreneurs-small business). Simply put, reseller hosting is the ability to provide hosting to your own clients as if you yourself were the web hosting company. This is typical for aspiring entrepreneurs who want to start their own web hosting firm or for current web developers and designers who desire to add additional services to their brand.
2. How does reseller hosting work?
Answer : Here are the (perhaps over-simplified) steps to establishing a reseller business: 1. Research and select a hosting company. 2. Purchase the reseller package that meets the goals of your business. 3. Know and understand your target market to locate your new customers. 4. Create your own branded hosting packages. 5. Decide your price. 6. Sell hosting packages to your clients. 7. Earn profit
3. What’s included in a reseller package?
Answer : Below are some of the common features often included in Reseller packages: 1. Disc Space 2. Bandwidth 3. Domain Hosting 4. Ability to brand your own web hosting company with the hosting provider company unknown to your client (also known as “white label”) 5. Latest cPanel control panel. 6. Manage your own plans and configure different accounts based on your needs. 7. Pass on features to your own clients such as email, control panel, additional scripts and monitoring tools. 8. Premium support (usually 24/7) offered by hosting providers.
4. Will my clients know it’s me…or my hosting company?
Answer : They will believe it’s you! You see, you can run your own hosting business under your banner and brand without your clients knowing who your actual upstream hosting provider is. This gives you total control in promoting your business with your name written all over it!
5. Do I need to be a hosting expert to succeed at this?
Answer : Nope. Your provider will handle all the backend, “dirty” work, so you can focus on building your business. Server hardware, connectivity, network infrastructure, hardware setup and maintenance, security and updates for your servers are all addressed by your web hosting provider. It’s a good idea to check into these things as you do your research to ensure that you’ll receive the best tech support if certain issues arise…and they likely will.
6. If my business grows, can I upgrade at any time?
Answer : Absolutely…you can upgrade your reseller hosting account at any moment to expand with the demands of your business.
7. How do I get started?
Answer : To get started, you simply follow the steps outlined in FAQ-2. The foundation to your success will lie in choosing a good reseller web hosting provider that not only meets the objectives of your business, but can provide you with consistent, reliable service and support because it's your name that is on the line when dealing with your customers. Choose wisely…which leads to the final FAQ…
8. How do I choose the best hosting provider?
Answer : It’s important to know that you can offer your own customers the best possible web hosting experience prior to building your clientele. Here are just some qualities to keep in mind when searching for your reseller web hosting service: 1. Easy to use cPanel 2. At least 1 site builder 3. Satisfaction guarantee 4. Private nameservers 5. Brandable client panel 6. 24/7/365 impeccable support 7. A 99.999% uptime guarantee 8. Fully managed services
Conclusion
In sum, reseller hosting can be lucrative if you’re looking to get into the web hosting business or if you’re a developer or designer. However, it is a lot of work and is certainly not for everyone. Make sure you research web hosting service providers to ensure they can offer your site optimal performance and make sure you’re comfortable with advanced website controls.
List of Reseller Web Hosting Service Providers:
Read More : You can explore here 30+ Best Web Hosting Providers 2023
Video - Best Web Hosting For Small Business
Affordable Website Hosting for your domainIf you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
6 Types of Website Design for your Website or Blog
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
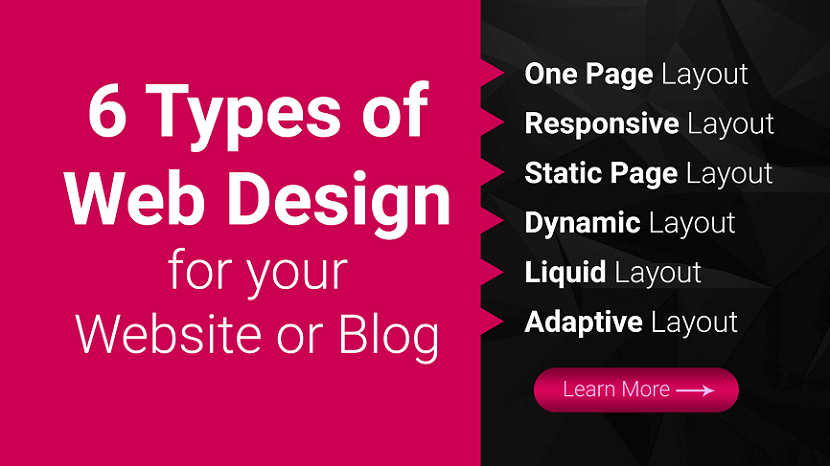
With 94% of first impressions relying on website design, you must create a beautifully crafted website for your business or blog. But when you get started with web design service or looking for a web design package, you may not know what approach to take with your website. What types of web design are best for your business or blog?
Luckily for you, we have got all the answers. Keep reading to learn about six types of web design and the pros and cons of each:
- One Page Website
- Responsive Website
- Static Website
- Dynamic Layout
- Liquid Website
- Adaptive Website
Plus, we will cover the different types of websites you can create, so you can determine which one is best for your business! Need some marketing inspiration?
Subscribe to our email newsletter for more updates!
6 Types of Web Design for your Website or Blog
Ready to build your website but are not sure which web design format is best? Here are six of the most common web design layouts for your business and the pros and cons of each.
1. One Page Website
We will cover on our list of types of web design as a one page layout website. As the name implies, a one page layout website uses only a single page that users scroll down to find information about your products or services. With this design layout, you can have a “Navigation Menu” with links to specific points of your page.
Pros of Single Page Website:
- Easy to create.
- Can help you create a clean and simple website.
Cons of Single Page Website:
- Can not be used for businesses that sell products online.
- Can not be used for companies that need multiple pages.
- Can deter people away if the single page is too long and requires too much scrolling.
2. Responsive Website
Next on our list of types of website layouts is responsive design layout website. This layout format is the most popular type, as it allows your site to accommodate all devices and fill the browser size perfectly. Responsive design is built with a mobile first approach.
You create your mobile layout first, and then you expand your website for bigger browser sizes. So instead of trying to trim down your website and make it smaller, you start small and build it bigger.
Pros of Responsive Website:
- Get a website that’s built for mobile users.
- Delivers a seamless experience on all devices.
- Do not have to build a separate mobile site.
Cons of Responsive Website:
- Takes more time to build and develop.
3. Static Website
Most basic type of website design is a static page layout website. With this layout, you build a website with pre-set page dimensions. It has a permanent width. Static layouts stick to these dimensions, regardless of the browser or device type.
Static layouts have phased out with the rise of mobile usage. Since these sites do not adapt to devices, they do not provide a positive user experience on smartphones or tablets. While static layouts are still an option, you typically do not want to use them unless you are creating a completely separate mobile version of your site.
Pros of Static Website:
- Easy to set up.
Cons of Static Website:
- Not responsive to devices or browsers.
- Requires creating a separate mobile site (more work).
4. Dynamic Website
When you look at a list of the types of web design, you will see that the dynamic website layout is an option. Dynamic website layouts are great for people who do not have extensive HTML knowledge. These websites can deliver different content to website visitors, even if two separate people look at the same page.
With a dynamic website vs. static website, you build a database of information and features. Then, when a user requests a page, the web coding automatically works to put the components together from your database to form the webpage.
Pros of Dynamic Website:
- Interactivity with users.
- Increased functionality for users.
- Less coding skills required.
Cons of dynamic Website:
- Can be more complex to set up with different functionalities.
- Tend to load slower because of all the different elements and page compositions.
5. Liquid Website
Next on this list of types of website design is liquid design layout website. This layout, also known as Fluid Design, uses flexible units rather than the fixed units static layouts use. Since the units are flexible, the page will always fill the width with the device’s screen, regardless of what device it is.
Because user experience is critical to your site driving and engaging traffic, liquid layouts have also started to phase out as a viable option for businesses. While you can still use this layout, you risk delivering a poor user experience from your site stretching too far or squishing information together on the page.
Pros of Liquid Website:
- Easier to set up than responsive design
- No information gets cut off on pages
Cons of Liquid Website:
- If a browser is really wide, information gets stretched to fit the screen and can look unappealing
- If a browser is smaller, information gets smooshed together to fit the screen, making it difficult to read and browse
6. Adaptive Website
One web design format you can use for your site is adaptive website layout. As the name implies, this website uses CSS queries to adjust the website’s size to detect the size of the browser. Adaptive websites will automatically alter the website’s layout to provide the best user experience for visitors.
With adaptive website layouts, there are set parameters for how a website will adjust. For example, a set parameter may look like this: “If the browser is 500 pixels wide, set the main content container for 400 pixels wide.” For example, if you have a website with a two-column layout, the adaptive layout would change into a single-column design on a small browser screen.
Pros of Adaptive Website:
- Easy to set up.
- Takes less development time than responsive layouts.
- Can adjust your website according to each browser size.
Cons of Adaptive Website:
- Device widths in between set points can cause your site to have too much space or not enough space.
- Is not fully responsive.
Types of website layouts
Here is a list of different website layouts and which sites benefit the most from them:
1. F-shape layout
The f-shape layout creates a website design that follows the general viewing pattern of the site's visitors. Scientific studies have found that website users often view and move their eyes across a web page creating an F or E shape. Webpages that design their layout to match those instinctive eye movements can help capture visitors' attention more naturally. These types of layouts are most common for websites that display a lot of options for users to choose from, such as news websites and search engines, allowing users to scan the options quickly and make a decision.
2. Z-shape layout
The z-shape layout is very similar to the f-shape layout, except it targets a different group of individuals. Scientific studies have shown that individuals from western cultures use a z shape with their eyes more often than an f shape to navigate the pages of different websites. Z-shape layouts are often most effective for websites that have a singular goal, such as having consumers sign up for a service or purchase a product. Creating a button that navigates users to the next step of company interaction and placing it along the z-shape path can help increase customer outreach and revenue.
3. Grid of cards layout
A grid of cards layout displays information in a grid system that users or website visitors can easily manipulate by adjusting the size of the browser window or screen. Some of the most common sites that use a grid of cards layout are video streaming websites that display image previews for their different video options. They display each of the previews as cards in a grid system, and the number of visible video options changes based on the size of the screen.
A grid layout is great for websites, like video streaming services, that display a lot of options and information of equal value, which can help users find what they're looking for more easily.
4. Boxes layout
The boxes layout uses one larger box as a website's header, which displays an image and two smaller boxes underneath that provide additional images or information for users. Each box gives the user important or engaging information about the company's or website's purpose and links the user to other dynamic web pages they can explore to find more helpful information. Because the boxes can prominently display images, artists often use this layout to show their portfolio and businesses use it to display featured products.
5. Split screen layout
A split screen layout divides a website into two sections that users can choose to explore. This layout works well for companies and organizations that have two pieces of content that are equally important to their business and consumers. For example, a clothing company that sells women's and men's clothing might use the split screen layout to advertise their products. Having both options on the front webpage can allow users to pick which one they're looking for quickly and continue exploring the site.
6. Fixed sidebar layout
The fixed sidebar layout places a stationary menu of options for users on the left or right side of the webpage. This sidebar menu provides visitors with quick and helpful navigation choices, allowing them to explore the website more easily. The fixed sidebar layout often works best with websites that have a limited number of webpages to choose from, such as businesses that sell one major product. For example, if a company that sold watches used a fixed sidebar, some of their menu options could include: about us, online store and contact us.
7. Magazine layout
The magazine layout uses a design that resembles printed publications. This design displays a lot of information to visitors by using a system of columns and grids to help individuals navigate the webpage more easily. The magazine layout is often used by publication companies to resemble how their product might look in its printed form, which can help create a fun and engaging format for users, motivating them to continue reading and exploring.
8. Asymmetrical layout
Asymmetrical layouts ensure that the webpage promotes an uneven design, meaning one half of the page is often larger than the other. Companies and organizations often use this layout to create an aesthetically pleasing web page while directing users to a certain area of the site.
For example, a business might use the larger section of the website to display an image or company slogan, while using the smaller side to encourage users to fill out their contact information to learn about special sales and promotions. The smaller section often attracts the visitor's attention, encouraging them to engage with the website or company. Because of its ability to entice users, the asymmetrical layout is often used on a website's homepage.
Featured image layout
The featured image layout places a prominent and large image at the top of the webpage to attract users. Most often, the featured image is a picture of a popular product that a company or business is selling. Companies that sell aesthetically pleasing products often use this type of layout to immediately attract visitors' attention and encourage them to make a purchase. For example, a company that sells computers might use a featured image layout to display their computers' design and style.
10. Curated visuals layout
The curated visuals layout uses illustrated images to promote a product or service. Companies and organizations often use this layout to display a certain emotion they want users to feel when they use the webpage. This type of advertising strategy can help consumers feel motivated to interact with the company and possibly purchase their goods and services. Most often, businesses or companies with a complicated service that's difficult to sell might use curated visuals to help ease the experience and relay necessary information to users.
Types of websites
4 Types of websites you can create
In addition to narrowing down your list of types of website layouts to the best one, you also must determine what kind of website you need to create for your business. Every business has different needs, which means your site type may differ from others.
Here are four types of websites you can create for your business:
1. Business websites
First on our list is the type of website you can create as a business website. A business website is a standard site. It contains information about your company and the services you offer. If you do not sell products online, you may also build a business site just to showcase what you offer.
These sites are simple and serve as a hub for people to learn about your business. You can use this website type if you are not selling products on your website. For a business website, you can use any of the types of web design listed above. You will want to choose the ones that help you deliver the best experience for your audience.
2. Blog
Second on our list is the type of website you can create as a blog. Blogs are websites that share helpful information with readers about topics in their industry. While a blog may not be your company’s primary website, you may consider creating a blog site if you are doing content marketing.
Content marketing is a crucial strategy for helping your business grow online and build trust with your audience. You may consider having a separate blog website, or integrating it into your core website to help you take advantage of the benefits of content marketing.
This website type can use any type of web design format, except for one page layout website.
The best types of web design layouts for this website type are adaptive and responsive.
3. Ecommerce websites
Another type of website you can create for your business is an ecommerce website. This website type is best for your business if you want to sell products on your site. Ecommerce sites are built to host product pages, add products to a cart, and complete transactions.
If you’re looking to sell products, this website type is best for your business.
In terms of the best types of web design for an ecommerce website, responsive and adaptive are most suitable for an ecommerce site.
4. Membership websites
The last type of website you can create is a membership website. With this website type, you have a paywall for people to enter. Only people who have a membership can enter your site and see your products.
A1truejobs.com is a membership website example. You must create an account and pay the membership fee and become a member of the site.
If you want to use this website type, you can use two types of web design layouts: adaptive or responsive.
Need help figuring out which type of web design is best for you?
With so many types of web design available, it’s challenging to know which type is best for your business. If you’re feeling overwhelmed with building the best website, RGB Web Tech can help you to create a beautiful web design for your business or blog.
Our team experts can help you craft a beautifully designed website that delivers the best experience for your audience. Ready to build your dream website? Contact us online or call us today at +91-9878585860 to speak with a strategist about our web design services and affordable web design packages
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
What is Graphic Design? Beginner Guide
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
Graphic design is the art and practice of creating visual content to communicate messages. Designers use typography, imagery, color, and layout techniques to craft compelling and effective designs for various media, including print, digital, and environmental graphics. The primary goal is to convey information clearly and engagingly while evoking the desired emotional response from the audience. Graphic design encompasses a wide range of applications, from advertising and branding to web design and product packaging. It requires a blend of creativity and technical skills, often involving software like Adobe Creative Suite. Effective graphic design is essential for businesses and organizations to establish their identity, attract customers, and deliver their messages efficiently. It combines aesthetics and functionality, making it a crucial element in modern visual communication.
Contents Overview
- What is the Main purpose of graphic design?
- What are the Elements of Graphic Design?
- What are the Principles of Graphic Design?
- What are the tools of graphic design?
- What are the Types of Graphic Design?
- Common graphic design jobs
- What does a graphic designer do?
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is the Main purpose of graphic design?
The main purpose of graphic design is to communicate messages visually in a clear, engaging, and effective manner. It involves the strategic use of typography, imagery, color, and layout to convey information and evoke specific responses from the audience. Graphic design aims to inform, persuade, and captivate viewers, making it a crucial tool for businesses and organizations. It helps establish brand identity, attract and retain customers, and enhance the overall user experience across various media, including print, digital, and environmental graphics. Ultimately, the goal of graphic design is to deliver a message that resonates with the target audience and achieves the desired outcome.
What are the Elements of Graphic Design?
Graphic design relies on several key elements to create visually appealing and effective designs. These elements include:
- Line: Lines are used to create shapes, divide spaces, and guide the viewer's eye. They can be straight, curved, thick, thin, solid, or dashed.
- Shape: Shapes are created by lines and can be geometric (circles, squares, triangles) or organic (freeform, natural shapes). They help to structure the design and can convey different meanings.
- Color: Color influences mood and perception. It is used to attract attention, create harmony, and convey emotions. Color theory involves understanding the relationships between colors and how they interact.
- Texture: Texture refers to the surface quality of an element. It can be visual (simulated) or tactile (physical). Texture adds depth and interest to a design.
- Space: Space refers to the area around and between elements in a design. Positive space is the space occupied by elements, while negative space (or white space) is the empty space around them. Proper use of space creates balance and clarity.
- Form: Form adds depth and dimension to a design. It is often achieved through shading, perspective, and the use of light and shadow to create the illusion of three-dimensionality.
- Typography: Typography is the art of arranging type to make written language legible, readable, and visually appealing. It involves selecting fonts, adjusting spacing, and designing the overall text layout. Check out free fonts to create awesome designs!
- Balance: Balance is the distribution of visual weight in a design. It can be symmetrical (evenly distributed) or asymmetrical (uneven but still balanced). Balance creates stability and structure.
- Contrast: Contrast involves the difference between elements, such as color, shape, size, and texture. High contrast draws attention and emphasizes important elements, while low contrast creates a harmonious and subtle design.
- Hierarchy: Hierarchy is the arrangement of elements to show their order of importance. It guides the viewer's eye through the design, ensuring that the most important information is noticed first.
- Alignment: Alignment refers to the placement of elements in relation to each other. Proper alignment creates a cohesive and organized look, making the design more visually appealing and easier to navigate.
- Repetition: Repetition involves using the same or similar elements throughout the design to create consistency and unity. It helps to reinforce the overall message and makes the design more cohesive.
What are the Principles of Graphic Design?
The principles of graphic design are fundamental guidelines that help designers create visually appealing and effective compositions. These principles include:
- Balance: Balance involves distributing elements evenly within a design to create a sense of stability. It can be symmetrical (equal distribution) or asymmetrical (different but balanced elements).
- Contrast: Contrast is the difference between elements, such as color, size, shape, and texture. It helps to create visual interest, highlight important areas, and distinguish elements from one another.
- Emphasis: Emphasis is about creating a focal point in the design to draw attention to the most important elements. This can be achieved through contrast, color, size, and placement.
- Movement: Movement guides the viewer's eye through the design in a deliberate path. It can be achieved through lines, shapes, and positioning of elements, ensuring that the viewer's attention flows smoothly from one part of the design to another.
- Repetition: Repetition involves using the same or similar elements consistently throughout the design. It creates unity, reinforces concepts, and helps to establish a visual rhythm.
- Proportion: Proportion refers to the relative size and scale of elements within a design. It ensures that elements are appropriately sized in relation to each other, creating a sense of harmony and balance.
- Alignment: Alignment is the arrangement of elements to create a clean, organized, and cohesive look. Proper alignment ensures that elements are visually connected and related to each other.
- Unity: Unity is the harmony between all elements in a design, making them appear as a cohesive whole. It ensures that all parts of the design work together and support the overall message.
- Variety: Variety involves incorporating different elements and styles to create interest and avoid monotony. It can be achieved through contrasting colors, shapes, textures, and sizes.
- Hierarchy: Hierarchy is the organization of elements to show their order of importance. It guides the viewer's eye from the most important information to less critical details, helping to communicate the message effectively.
What are the tools of graphic design?
Graphic designers use a variety of tools to create their work. These tools can be broadly categorized into software, hardware, and traditional tools. Here's a comprehensive list:
Software Tools
1. Adobe Creative Suite:
- Photoshop: For photo editing, image manipulation, and digital painting.
- Illustrator: For vector graphics, illustrations, and logo design.
- InDesign: For layout design, such as magazines, brochures, and books.
2. CorelDRAW: A vector graphics editor used for design and illustration.
3. Sketch: A digital design tool for creating interfaces and user experiences.
4. Figma: A collaborative interface design tool used for prototyping and UI/UX design.
5. Affinity Designer: A vector graphic design software alternative to Adobe Illustrator.
6. Canva: An online platform for creating social media graphics, presentations, posters, and other visual content.
7. Procreate: A digital illustration app for iPad, popular among illustrators and artists.
8. GIMP: An open-source image editor similar to Adobe Photoshop.
Hardware Tools
1. Computer: A powerful desktop or laptop is essential for running graphic design software.
2. Graphics Tablet: Devices like Wacom tablets allow for precise drawing and illustration directly into software.
3. Monitor: High-resolution monitors with accurate color representation are crucial for design work.
4. Scanner: Used to digitize sketches, drawings, or printed materials.
5. Printer: High-quality printers are essential for producing physical copies of designs.
Traditional Tools
1. Sketchbooks and Paper: For brainstorming, sketching ideas, and initial drafts.
2. Pencils and Pens: Essential for drawing, sketching, and inking designs.
3. Markers and Brushes: Used for adding color and texture to sketches and illustrations.
4. Rulers and Compasses: For creating precise lines, shapes, and measurements in traditional design work.
Online Resources and Libraries
1. Stock Photo Websites: Platforms like Shutterstock, Unsplash, and Adobe Stock provide high-quality images for use in designs.
2. Font Libraries: Websites like Google Fonts, Adobe Fonts, and DaFont offer a wide range of typefaces for various design projects.
3. Color Palettes: Tools like Adobe Color help designers choose and create harmonious color schemes.
What are the Types of Graphic Design?
Graphic design encompasses a wide range of specializations, each serving different purposes and industries. Here are some of the main types of graphic design:
- Visual Identity Graphic Design: This type involves creating brand elements such as logos, color schemes, typography, and brand guidelines to establish a cohesive visual identity for a company or organization.
- Marketing & Advertising Graphic Design: Designers in this field create visuals for promotional materials like flyers, brochures, posters, banners, social media ads, and email campaigns to attract and engage customers.
- User Interface (UI) Graphic Design: UI designers focus on the visual aspects of user interfaces for websites, apps, and software, ensuring an attractive and intuitive user experience.
- Publication Graphic Design: This includes designing layouts and covers for printed and digital publications such as books, magazines, newspapers, and e-books, focusing on typography, imagery, and overall layout.
- Packaging Graphic Design: Designers in this area create the visual aspects of product packaging, including the shape, graphics, colors, and typography, to protect the product and attract customers.
- Motion Graphic Design: This involves creating animated graphics for videos, television, websites, and other multimedia platforms. It includes elements like animation, visual effects, and cinematic techniques.
- Environmental Graphic Design: This type merges graphic design, architecture, and interior design to create visually engaging environments. Examples include signage, wayfinding systems, exhibition designs, and themed environments.
- Art and Illustration for Graphic Design: This specialization involves creating original artwork for various contexts, such as posters, t-shirts, album covers, book illustrations, and digital art.
- Web Design: Web designers create the layout, visual design, and interactive elements of websites, focusing on aesthetics, usability, and the overall user experience.
- Information Graphic Design (Infographics): Designers create visual representations of data and information, making complex data more accessible and easier to understand through charts, diagrams, and maps.
- Typography: Typography designers specialize in creating and arranging type to make text readable, appealing, and effective in communication. They work on designing typefaces, fonts, and other text-based elements.
- Corporate Design: This involves designing corporate identity materials like business cards, letterheads, envelopes, and other stationery that represent a company's brand.
Common graphic design jobs
Graphic design offers a variety of career opportunities across different industries. Here are some common graphic design jobs:
- Graphic Designer: Creates visual content for various media, including print, digital, and social media. They work on projects such as logos, brochures, advertisements, and websites.
- Art Director: Oversees the visual style and creative direction of projects. They manage design teams and ensure that the overall visual presentation aligns with the client's or organization's goals.
- Creative Director: Responsible for the overall creative vision of a project or campaign. They lead the creative team, make high-level creative decisions, and coordinate with clients or stakeholders.
- UI/UX Designer: Focuses on designing user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX) for websites, apps, and software. They ensure that products are visually appealing, intuitive, and user-friendly.
- Web Designer: Specializes in creating the visual design and layout of websites. They work on elements like graphics, color schemes, typography, and overall site structure to ensure an engaging user experience.
- Motion Graphic Designer: Creates animated graphics and visual effects for videos, films, television, and online media. They use animation software to bring static designs to life.
- Brand Identity Designer: Develops visual elements that represent a brand's identity, including logos, color palettes, typography, and brand guidelines. They ensure consistency across all brand materials.
- Illustrator: Produces original artwork for various applications, such as books, magazines, advertisements, and digital media. They create detailed illustrations and visual concepts.
- Packaging Designer: Designs the visual and structural aspects of product packaging. They create packaging that is both functional and visually appealing to attract customers and protect the product.
- Publication Designer: Works on the layout and design of printed and digital publications, such as books, magazines, newspapers, and e-books. They focus on typography, imagery, and overall page design.
- Environmental Graphic Designer: Merges graphic design with architecture and interior design to create visually engaging environments. This includes designing signage, wayfinding systems, and exhibition displays.
- Infographic Designer: Specializes in creating visual representations of data and information. They design charts, diagrams, and maps to make complex information more accessible and understandable.
- Freelance Graphic Designer: Works independently, offering design services to various clients on a project-by-project basis. They may work in multiple areas of graphic design depending on their skills and client needs.
- Marketing Designer: Creates visual content for marketing campaigns, including social media graphics, email templates, advertisements, and promotional materials. They work closely with marketing teams to ensure consistent messaging.
- Visual Designer: Focuses on the overall aesthetics of a project, working on both web and print designs. They ensure that the visual elements align with the brand's identity and communication goals.
What does a graphic designer do?
A graphic designer uses visual elements to create designs that communicate messages effectively and aesthetically. Their responsibilities can vary widely depending on the specific job and industry but generally include the following tasks:
- Understanding Project Requirements: Collaborating with clients, marketing teams, or other stakeholders to understand the project's goals, target audience, and specific requirements.
- Concept Development: Brainstorming and developing creative concepts that align with the project’s objectives. This often involves sketching ideas, creating mood boards, and exploring different design approaches.
- Creating Visual Content: Using design software to create graphics, layouts, and illustrations. This can include logos, brochures, advertisements, websites, social media graphics, packaging, and more.
- Selecting Colors, Fonts, and Images: Choosing appropriate color schemes, typography, and imagery that enhance the overall design and ensure brand consistency.
- Layout and Composition: Arranging text, images, and other design elements in a way that is visually appealing and easy to read. This involves understanding principles of balance, contrast, alignment, and hierarchy.
- Prototyping and Mockups: Creating prototypes or mockups of designs to present to clients or stakeholders for feedback. This can include digital mockups for websites and apps or physical mockups for print materials.
- Revising and Refining Designs: Making revisions based on feedback from clients or stakeholders. This iterative process ensures that the final design meets all requirements and expectations.
- Preparing Final Files: Ensuring that all design files are properly formatted and ready for production, whether for print or digital use. This includes exporting files in the correct resolution and format.
- Collaborating with Other Professionals: Working with other creative professionals such as photographers, illustrators, web developers, and printers to bring the design to life.
- Keeping Up with Design Trends: Staying informed about current design trends, tools, and technologies to ensure that their work remains fresh and relevant.
- Project Management: Managing multiple projects simultaneously, meeting deadlines, and ensuring that all aspects of the project stay on track.
FAQs
1. What is graphic design?
Answer : Graphic design is the art and practice of creating visual content to communicate messages. It involves the use of typography, imagery, color, and layout techniques to produce designs for various media, including print, digital, and environmental graphics.
2. What does a graphic designer do?
Answer : A graphic designer creates visual content to communicate messages effectively and aesthetically. They work on projects such as logos, brochures, websites, advertisements, and packaging. Their tasks include concept development, creating designs using software, selecting colors and fonts, and collaborating with clients and other professionals.
3. What software do graphic designers use?
Answer : Graphic designers commonly use software like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign. Other popular tools include CorelDRAW, Sketch, Figma, Affinity Designer, Canva, and Procreate.
4. What are the key elements of graphic design?
Answer : The key elements of graphic design include line, shape, color, texture, space, form, typography, balance, contrast, hierarchy, alignment, and repetition. These elements work together to create visually appealing and effective designs.
5. What are the principles of graphic design?
Answer : The principles of graphic design include balance, contrast, emphasis, movement, repetition, proportion, alignment, unity, variety, and hierarchy. These principles guide the organization and arrangement of design elements to achieve a cohesive and effective visual composition.
6. How do I become a graphic designer?
Answer : To become a graphic designer, you typically need a combination of education and practical experience. Many graphic designers have a degree in graphic design or a related field. Building a strong portfolio, learning design software, and gaining experience through internships or freelance work are also important steps.
7. What is the difference between UI and UX design?
Answer : UI (User Interface) design focuses on the visual aspects of a product, such as layout, colors, and typography. UX (User Experience) design, on the other hand, is concerned with the overall feel of the product, including usability, accessibility, and the user's interaction with the product. Both UI and UX designers work together to create seamless and enjoyable user experiences.
8. What is a brand identity?
Answer : Brand identity is the collection of visual elements that represent a brand, including its logo, color palette, typography, imagery, and overall style. It helps to create a cohesive and recognizable image for the brand, distinguishing it from competitors.
9. How important is color in graphic design?
Answer : Color is a critical element in graphic design as it influences mood, perception, and brand recognition. It can attract attention, convey emotions, and create visual harmony. Understanding color theory and how colors interact is essential for effective design.
10. What is the role of typography in graphic design?
Answer : Typography involves the selection and arrangement of type to make written language legible, readable, and visually appealing. It plays a crucial role in establishing hierarchy, setting the tone, and enhancing the overall aesthetic of a design.
11. What are some common graphic design jobs?
Answer : Common graphic design jobs include graphic designer, art director, creative director, UI/UX designer, web designer, motion graphic designer, brand identity designer, illustrator, packaging designer, publication designer, environmental graphic designer, and marketing designer.
12. What is the difference between raster and vector graphics?
Answer : Raster graphics are made up of pixels and are resolution-dependent, meaning they can lose quality when scaled. Examples include photographs and digital paintings. Vector graphics, on the other hand, are created using mathematical equations and can be scaled indefinitely without losing quality. Examples include logos and illustrations created in Adobe Illustrator.
Conclusion
Graphic design is a dynamic and multifaceted field that plays a crucial role in today's visual communication landscape. By combining artistic creativity with technical skills, graphic designers create compelling visual content that informs, persuades, and captivates audiences across various media. Understanding the elements and principles of design, mastering essential tools, and staying updated with industry trends are vital for success in this profession.
Graphic design encompasses diverse specializations, including branding, marketing, web design, and environmental graphics, each requiring a unique blend of creativity and technical expertise. Whether crafting a logo that defines a brand's identity or designing a user interface that enhances digital experiences, graphic designers shape the way we perceive and interact with the world around us.
In an increasingly visual culture, the demand for skilled graphic designers continues to grow. Aspiring designers must cultivate their skills, build a strong portfolio, and stay adaptable to the ever-evolving design landscape. Ultimately, graphic design is about solving problems through visual communication, making it an indispensable discipline in our modern, visually-driven society.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
10 Essential Tips to Improve Your Website Design
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

You have about 5-seconds (give or take) to let your website visitors know what your company or brand is and what they do. Is your website easy to navigate? Is the layout of your pricing easy to see and understand? Do you have a high bounce rate? It may be time to improve website design.
If the answer to all of the above questions is “no,” it might be time to take a hard look at the way you’ve been designing and optimizing your website. It never hurts to go over website improvement ideas, especially if you are trying to learn how you can improve the layout.
So much of today’s business is conducted online. From shopping to marketing, to communicating with providers, people depend on the Internet to help them perform everyday tasks. Without a website, businesses, blogs and brands are destined for failure.
Developers like yourself have numerous ways to improve website design. Even if you have a clean, smooth, professional website, that doesn’t mean it is converting how you want.
You should always consider website improvement ideas as time goes by.
When it comes to designing, you want to make sure the layout conveys the right message without overwhelming visitors.
10 Tips to Improve Website Design
There is a lot of information out there about ways to improve website design. Narrowing it down can be difficult. You want to make sure you cover the most important website design tips out there.
These are 10 essential tips to improve your website design. So, when you ask yourself… “How can I improve my website,” these are the ones you definitely want to review and implement.
1. Mobile Friendly and Responsive
There really is no argument here. Of course, you want several things in place to improve your website design. But no matter what anyone tells you, a mobile friendly and responsive website should be at the top of your website design tips list.
Having a website that is not mobile friendly or responsive hurts you in several different ways. Not only does Google drop you in rankings (started in 2015) and searches, but you lose visitors anyway because they have a hard time looking at your content in certain formats.
While responsive and mobile friendly work together to create a streamlined user experience, they are actually two different things.
- Mobile Friendly: Your website can be viewed properly on any mobile device and looks correct on all phones and tablets.
- Responsive: Your website responds to screen size, browser choice and displays properly no matter what those are.
More than likely you have created a responsive and mobile friendly website by now. If you use WordPress or another popular platform for your website then you are definitely good to go.
However, if for some reason your site is not mobile friendly and responsive, this is the first website design tip you should tackle to improve the overall look, feel and functionality.
2. Simple Navigation
Look at this from a user’s perspective. How often do you visit a website and find the navigation is cloudy and muddled? Is it difficult to get around the site? Are menus, links and other information displayed all over the place?
It is important that you simplify the navigation for users. Even if you have a lot of content and need to map it out differently, simple navigation will give you a traffic spike almost immediately.
Here are a few things to remember when simplifying website navigation. These can be followed loosely, but following them closely will help.
- No more than 7 items in your main menu (this does not include the dropdown portions).
- Users should be able to access any point of the site from any other area within 3 clicks or less. It’s better to strive for two clicks, though.
- Be as descriptive as possible with your labels and links.
- Keep your navigation bar fixed.
When it comes to ways to improve your website, simplified navigation should be toward the top of the list. Remember, if your website users can access information and get around easily, they are going to stay on your website much longer.
3. Improve Page Speed
Your website page speed is crucial for keeping users on the site and interested. Remember, over 53% of people will abandon a mobile site if it takes longer than 3-seconds to load.
So, when you are making your site mobile friendly and responsive, you also want to take steps to improve website design by making sure your page speed is up to par.
This goes for any type of website you have. Blog, business, shopping cart, etc. Matter of fact, if you have even a 2-second delay in your load time during a transaction, the chances are that your potential customers will abandon carts and you will end up with one customer less than you started with.
There are several things you can do to optimize and speed up your website. Some of them include:
- Optimizing Images
- Reducing Plugins
- Cleaning Up Framework & Themes
- Use a CDN (Content Delivery Network)
- Optimize the Homepage
- Consider the Best Hosting Platform
- Use Redirects as Little as Possible
Page speed goes hand-in-hand with other ways to improve website design. Consider this a top priority when you are thinking about website design tips that will improve the functionality of your website.
4. Remove Unnecessary Content
Believe it or not, a massive amount of content is not always better. In many instances, less is actually more. This applies even more so when we talk about website design tips.
You want your website to be clean, smooth, professional and to the point. It’s all about walking the line of saying what you need without being visually overbearing.
You may have certain things you need to remove from the website. This is called unnecessary content. Getting rid of it will improve website design tremendously, as they do not follow website design best practices. Consider removing some of the following items if they are on your site:
- Complicated Animations
- Long, Muddled Content
- Stocky Web Images
- Over-Utilized Colors
Furthermore, it is a very good idea to be careful with the words you are using. If you can, go through your current content and look for the following words you may have used:
- Next Generation
- Flexible
- Robust
- Scalable
- Easy to Use
- Cutting Edge
- Groundbreaking
- Innovative
While these are not necessarily awful words, they are overused by hundreds, if not thousands of companies. They don’t make your content any more appealing or original.
5. Social Sharing and Social Follow
The world we live in these days has become a Facebook and Twitter world. That is to say, people connect and keep up with news and each other through social media.
Any website improvement ideas should involve taking advantage of social sharing and social following. Why? There are 800 million monthly active users on Instagram and 100 million daily active users on Twitter.
Those are astronomical numbers, but both come in behind Facebook, which has over 1 billion users. This is why it’s important for your website to offer social buttons to your visitors.
If by some chance you are unfamiliar with social sharing buttons, you need to get acquainted. They are the small buttons that are around the top or bottom of blog posts. They contain icons of different social media sites and allow you to share the page directly on the channel of your choice.
The idea is to get guests to share your content when they like what they read. Sharing content puts it out for everyone else to see without you having to do any work. This will allow your website to become more popular and gain site visitors that would have never known about you otherwise.
Social sharing options are a fantastic way to improve website design. This is one of the many tips that will quickly boost your social media engagement.
6. Strong and Visible Call to Action
Your website is a place to sell your products and services, pump your brand or blog, blog, blog. Make sure you have a strong and visible call to action in place. Give your site visitors a way to connect with your company.
A call to action can be a number of things including a free trial, account creation, linking them to buy something or have them sign up for a newsletter. A strong call to action will be the thing that increases your conversions, so make sure you put some time into coming up with the perfect one.
Other great examples of high converting calls to action include:
- Click here for more information.
- Download our sample xxxx.
- Sign up for a webinar.
- Watch the video.
- See all marketing services.
- See pricing.
A call to action can be in the form of a banner, buttons, a popup box or basically anything that helps grab the site visitor’s attention. They can even be full landing pages. Improve website design by giving site users something to do and let them interact with the site.
7. Use White Space to Your Advantage
Oftentimes people get nervous about white space on a website. In reality, you can use whitespace to your advantage and it should be a part of your layout.
Also called “negative space,” white space refers to the areas around elements on a page that are empty and lacking content or visual items. White space is an essential design element that helps you break up the page and increase readability.
Too often I come across websites with no white space. Elements, text and graphics run into each other and overflow. Every part of the main page is colored and used, and no white space is available.
This is a mistake.
If you have a front page or any page of your website that lacks white space, then you should review the layout. Strip the content and design, and create some white space to break up the content more appropriately. This will also make things more visually appealing to your site visitors.
With all the website improvement ideas floating around out there, this is one that could get lost in the mix.
Don’t let it. Proper use of white space is one of the better ways to improve website design.
8. SEO Strategy
You will hear people talk about SEO (Search Engine Optimization) all the time when it comes to ways to improve website design. While this visually will not affect the front of your website, it is extremely important to have a good SEO strategy in place.
Having proper SEO in place will do a number of things to improve your site. Most of all, it will allow you to rank higher in Google and will also allow you to trend for what you want and get properly indexed in search engines.
Also, consider an SSL certificate if your website does not already have one. Google has been pushing the https protocol and giving better ranking to sites that have these certificates.
Most website hosts will now offer a free version of the Let’s Encrypt SSL.
9. Have a Blog
One of the best ways for people to know what you do is by reading your content. Not only is a blog visually appealing to your site visitors, but also gives you a place to push content.
This is a great website design tip. So much so that oftentimes you will see older websites implement a blog, even after being online for years.
Having a blog on your site will also encourage user interaction and keep your potential customers engaged. You should post various articles that are relevant to your business and services.
Blog pages will generate more online traffic to your business website, which leads to more sales. It can also establish you as an authority in your industry, which will increase confidence in your services.
Remember to integrate your social share buttons within your blog section.
10. Use Color Theory to Your Advantage
Color theory and psychology matter and how they are used affects website conversion. Colors, how they are used and what they represent matter.
Use this to your advantage when you are designing or updating a website. Using color theory can add so much more to your site and is a website design tip that should not be ignored.
The standard language for color communication is called Pantone, and yes that is a real thing. You should know about it, and probably do if you are in the marketing field.
To help you a little, here is what colors represent:
- Red: passion, anger, love, confidence
- Orange: youthfulness, cheer, warmth, hunger
- Yellow: sunshine, happiness, energy, optimism
- Green: nature, fertility, balance, cleanliness
- Blue: water, tranquility, trust, power
- Purple: nobility, power, elegance, wisdom
- White: peace, balance, purity, simplicity, winter
- Gray: neutral, sophistication, balance, wisdom
- Black: exclusivity, modern, power, sophistication, mystery
- Brown: earth, stability, tradition, nature
- Pink: love, romance, femininity, baby girls, humanistic
- Turquoise: tranquility, clarity, compassion, healing
Final Thoughts
You have dozens of ways to improve website design at your disposal. You should at least entertain most of them if you haven’t already. The 10 website design tips that are listed in this article are ones I consider to be the most important and are the best ways to improve website design.
Start implementing some of these right away and you will notice a big change in visitor traffic and behavior.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
12 Principles of Design & How to works
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
You can’t just flip a switch and create beautiful designs on a whim. Like learning to walk before you run, there are certain fundamentals you’ve got to learn first.
The problem is that if you don’t have the time or inclination to take a design course, resources are pretty scarce. Sure you can rely on Canva templates, but even then you need to know how to use them properly.
This is why we've put together this post. It’s for you if you’ve ever wondered what goes into good design. You'll find it handy whether you're a complete amateur or a budding designer—so let's get stuck in.
What are design principles?
Design principles are guidelines to follow if you want to create effective visuals, from oil paintings and blog graphics to eye-catching social media posts.
Think of design as carpentry and these principles as your toolbox. You can use them to help you during the design process, and unlike hammers, nails and screwdrivers, they can exist entirely inside your head.
These tools give you a better understanding—and appreciation—of what goes into the designs we see every day. As you become acquainted with them, you’ll start to see what does and doesn’t work (and why), as well as how you can apply these principles to your own creative work.
What is "good design"?
We’re told that piece of art is subjective. For the most part, that’s true. But if you’ve ever seen an unintelligible parking sign or a website from the early days of the web, you’ll know there’s definitely such a thing as bad design.
As Jared Spool, an expert on design and usability, says, “good design, when it’s done well, becomes invisible. It’s only when it’s done poorly that we notice it.” This is why good design is tricky to define.
Luckily for us, in the late 1970s, an influential designer named Dieter Rams saw this problem. In response, he asked himself what constituted good design and came up with his own list of ten principles.
Little did he know, they would go on to inspire generations of designers, including Johnny Ive, the mastermind behind Apple’s most famous products.
Rams’s principles are:
- Good design is innovative
- Good design makes a product useful
- Good design is aesthetic
- Good design makes a product understandable
- Good design is unobtrusive
- Good design is honest
- Good design is long-lasting
- Good design is thorough down to the last detail
- Good design is environmentally friendly
- Good design is as little design as possible
You might notice that these principles are aimed at product design. Rams worked at Braun, so products were in his wheelhouse, but these principles are easily adapted to UX, UI, or any other design context.
Rams’s principles aren’t the only principles out there. Other notable design principles include Nielsen’s 10 usability heuristics and Whitney Hess’s five guiding principles for experienced designers.
The 12 principles of design
These are the building blocks graphic designers and artists use to put creative works together; the core principles of art that make up every design, from the fine art of the Louvre to the boxes of Corn Flakes at the local grocery store.
1. Balance
Where objects in real life carry physical weight, elements in design carry visual weight. Large elements are heavier and small elements lighter, with each element having its own "weight" based on how much attention they draw.
Visual balance is about ensuring your design is equally weighted on both sides of the central point. It’s like a seesaw—too much weight on either side and the whole thing becomes unbalanced.
By striking this balance you create visual harmony and stop your design from feeling too chaotic to the viewer. It’s one of the most important parts of visual composition, and comes in three basic forms:
Symmetrical balance
Symmetrical design uses an imaginary vertical (or sometimes horizontal) line to divide a design into two halves around a central point. Elements of equal visual weight are balanced on each side of the axis to create symmetry.
There are two variants of symmetrical balance: Reflectional symmetry, where the two halves are exact mirror images, and translational symmetry, where the same shape or elements are repeated on both sides of the design.
Asymmetrical balance
An asymmetric composition is when a design uses unequal weighted elements. One side might have a visually heavy element, balanced with multiple lighter elements on the opposite side.
To run with the seesaw example, it would be like having a 100kg weight on one side and 100 kg of feathers stacked on the other. It still achieves balance but provides a whole different experience.
Asymmetry is often more visually interesting. Where symmetrical designs can be quite static and predictable, asymmetrical balance can give designs a more dynamic feel.
Radial balance
Radial balance is when elements “radiate” from a point in the centre of a design. Think of rays shining from the sun, petals blossoming from a rose, or a squirt of tomato sauce in the middle of a juicy meat pie.
This form of symmetry is a way to add depth and movement to a design and works to draw attention to an object in the centre of a composition.
2. Emphasis
Emphasis is used to focus the viewer’s attention on a certain part of a composition. The effect is achieved by manipulating elements (like colour, shape and size) to make specific parts of a design stand out.
For example, say you wanted to bring attention to a call to action on a landing page. You could increase the text size and use colours that stand out from the background, emphasising the CTA and making sure visitors can’t miss it.
3. Repetition
As you may have already guessed, repetition refers to when an element is repeated throughout a design. It could be anything, from using a certain font colour to adding a repetitive pattern to a social media post.
Repetition makes designs visually exciting and cohesive. It also creates a sense of consistency by using a repeating motif that the viewer comes to expect. This makes it particularly useful when it comes to creating your distinct brand identity.
Brand identity is the visible element of your brand. The colours; design; logo. It acts to distinguish your company from the millions of others out there, so when folks see your designs they immediately know it’s your business.
Every successful business uses repetition. Why do we equate the swoosh and “just do it” with Nike? The blue can with Pepsi? Because these visuals were repeated so often that eventually they became synonymous with the brands they represent.
So while repetition can just help you make a sweet iPhone wallpaper, it’s a crucial tool for any company looking to build a visual identity and brand recognition.
4. Movement
When we think of movement we think of, well, things moving. A pendulum swinging. A Ferrari roaring down the freeway. But in design, it refers to the path a viewer’s eye takes when they look over a composition.
It’s not just what you look at; it’s the way you look at it. Designers can guide this by using lines, edges, shapes and colours to create focal points and encourage certain ways of seeing.
Movement can be harnessed to distract, direct and pull the viewer’s gaze around a design. By using subtle cues (particularly with lighting and perspective) a savvy artist can control this entire process. You can use lines to create directional cues and make images feel more alive.
5. Proportion
Proportion is the relationship between two or more elements in a design, particularly the size and scale of them. When things are "proportionate”, it means there’s a coordination between them that makes the design look aesthetically pleasing.
For example, when you’re reading a blog post you expect headings to be larger than the body text. Or if you were looking at a realistic drawing of a tortoise and a hare, you expect the hare to be larger than the tortoise.
Proportion is about finding harmony between two elements. You want to make sure things look “right”— that the elements look as if they belong together.
This is something that comes up when creating digital assets and websites online. It’s the bane of many an amateur designer’s existence. Here are a few tips for keeping the elements in your design in proportion:
- Assemble elements that are identical or share a function.
- Establish major and minor areas in the design to prevent monotony and boredom.
- Ensure size variations are subtle (unless the objective is emphasis.) Avoid separating the composition into halves, quarters, and thirds. Try to keep a sense of balance.
You can also play with proportions in a variety of ways to emphasise elements or get a certain message across. It’s a strategy you’ll notice advertisements do often and is usually best used for more creative projects.
6. White Space
\
The region between different design elements is referred to as "negative” or “white” space. This is part of the design that doesn’t contain anything. No images, drawings, shiny colours or text. Nothing.
The name is kind of misleading — it’s not a "negative" thing and it doesn’t have to be "white". It can be any colour: white space refers to what you don’t add; the empty parts around and within your design.
It’s one of the fundamental building blocks of design and is just as important as any elements you do include. Think of it like a diet: what you eat matters, but what you don’t eat matters just as much.
“White Space in design composition is the same as the use of silence in a musical composition. Without proportionate use of silence, music is unstructured. Similarly, without white space, design is unstructured and difficult to consume." — Mark den Hartog
There are two types of white space: micro and macro. Micro white space is the space between small elements (like text), while macro white space refers to the area between large elements or surrounding a design.
7. Contrast
Contrast is produced when two or more visual elements in a composition are different. It can be used to create specific effects, emphasise the significance of certain elements, and add visual appeal to your designs.
Designs that look the same are boring—by experimenting with contrasting colour hues, shapes, sizes, textures and typography, you can liven things up. Humans tend to like contrast. It’s a great way to grab attention, control the visual flow and keep folks engaged.
Keep in mind that adding too many variations can be confusing for viewers (the opposite effect you want to have.) As with most of the different elements of art, it’s about striking a balance.
8. Hierarchy
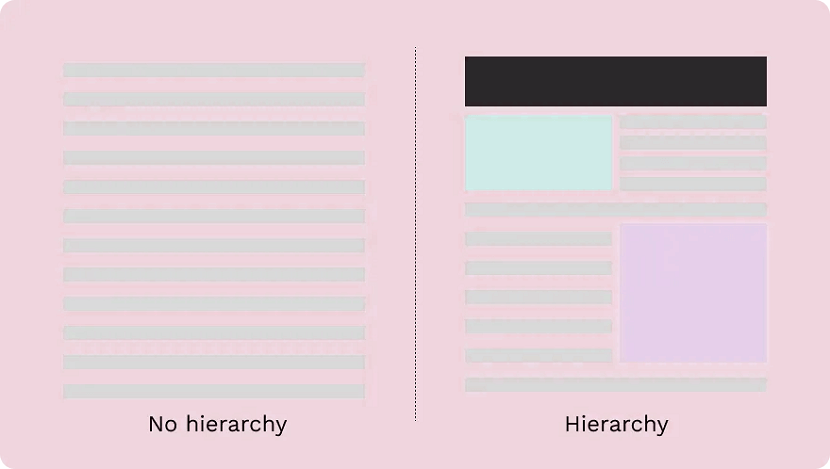
Visual hierarchy is about organising the value of the elements within your design. By ranking information from most important to least important, you make it easier for the viewer to digest your content.
This plays a critical role in UI and UX design. Ever noticed how most landing pages have the same layout? There’s a logo at the top, a menu at the top and then elements in descending order of importance below.
It’s not because they copied each other's homework—there’s a certain hierarchy that designers stick to in order to draw attention to the right things in the right order (and make it pretty to look at.)
The viewer’s eye should be drawn to the most important element first. These sit atop the throne at the top of the hierarchy, with the elements laid out below ranked in order of importance.
There are a number of visual tricks to influence this flow, including:
- Size and scale: The larger an element is the more likely a viewer is to see it. By making something smaller you can reduce its importance and put the emphasis elsewhere.
- Colour and contrast: A splash of colour makes a big difference. Use bright colours to make certain elements or information pop.
- Fonts: Use different typefaces and stylisations like italics and bold to draw the eye and move text higher or lower on the hierarchy.
- White space: White space enables you to give an element breathing room and make a central element stand out.
Patterns of hierarchy
People read a page in the same way: from top to bottom. But we don’t just stare blankly at s page and wait for information to register, we scan it.
The human eye tends to follow the same path during this process. For that reason, designers stick to two common patterns to make it faster to absorb information: the F-pattern and the Z-pattern.
The F-pattern applies to pages made up mostly of text, like an online or printed article. Readers scan in the shape of an “F”—first, with the headline across the top, then down the left side of the page and to the right as they identify things they find interesting.
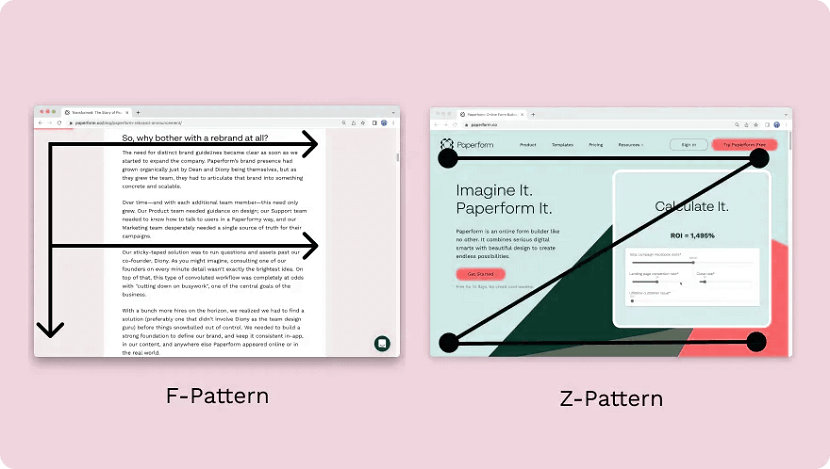
Designers use a Z-pattern for layouts with less text and more visuals. With this pattern, viewers scan across the top of the page and then diagonally down towards the opposite corner. They then scan the bottom in the same way as the top.
Most websites are designed in this way (including Paperform). Notice how the most important parts like the logo and navigation menu are at the top, while the secondary information like clients and chatbot is at the bottom.
9. Rhythm
Don’t worry, you can leave your dancing shoes at home. In design, rhythm hasn’t got anything to do with the way you move your hips. It’s about giving your composition a feeling of action and movement.
Designers create rhythm by repeating lines, shapes, colours and other elements. This makes a path for our eyes to follow, builds patterns and imbues the design with a sense of flow. There are a few different types of rhythm:
- Random rhythm: Repeating elements without any regular interval.
- Regular rhythm: When the elements are of a similar size and length and spread out over predictable intervals.
- Flowing rhythm: Natural patterns where the intervals are organic (like a tiger’s stripes or a bunch of flowers in a garden.)
- Progressive rhythm: A gradual change or sequence of elements that change over a series of clear steps (like a colour gradient for example.)
Rather than letting the viewer’s eye settle on a focal point, rhythm encourages viewers to move their eyes across the entire piece, following the lines and forms to their natural endpoints. It’s something you see reflected across nature and works of art.
10. Pattern
People tend to get confused between repetition in patterns, which is understandable, as they both deal with repeated elements. But the similarities end there.
While repetition occurs when the same elements are repeated throughout a design, a pattern is composed of different components repeated in the same way. Think of the way gift wrapping is usually made up of a few different repeated elements—that's a pattern.
You'll also notice patterns commonly used as backgrounds on websites and in mobile applications.
As a general rule, it's best to use colours, textures and shapes to create patterns. Try to avoid doing so with words — it tends to just give folks headaches. Despite the occasional bright colours and wacky designs, the key to creating effective patterns is simplicity.
11. Variety
Variety isn’t just the spice of life—it’s the spice of design too. It’s integral not to revert to the same old elements within a design to make sure things are visually interesting for your viewers.
Variety keeps things engaging. It stops designs from being stagnant, predictable and downright boring — all things you want to avoid. By making sure elements are varied you stop designs from feeling monotonous and uninspired.
The easiest way to do this is through juxtaposition and contrast. Place bright colours next to lighter hues, text next to images, and round shapes next to square ones. By doing so you can keep viewers engaged and your design interesting.
12. Unity
We've put unity last on this list for a reason—it only occurs when all the various elements within a design coexist to form a holistic experience that’s pleasing to the eye.
Unity adds order and makes a piece feel like a coherent whole, instead of a messy combination of individual parts that just so happen to exist on the same page. It's developed both visually and conceptually.
- Visual unity. An extension of “harmony”, is about elements working together, like colour schemes, the use of complementary styles, and in some cases, the repetition of colours and elements to achieve consistency. An example would be using the same colours for all the buttons on a webpage to keep the design cohesive.
- Conceptual unity. Is when you combine elements for the user’s convenience; it’s about blending form and function in a natural way. An example of this is how you can double-tap on Instagram to “Like” an image—it reduces friction and requires less action from the user.
To achieve unity you need to look out for three things: whether the elements you’ve used have a good reason to be there, whether they work together, and whether the message or concept you’re trying to display is communicated clearly.
By making sure your designs unite you reduce cognitive load and ensure viewers actually understand whatever it is your design is trying to achieve.
Put these design principles to work
Hopefully, these 12 design principles can help inspire you to take your creative work to the next level.
No matter what you’re designing—from product pages to actual products—if you take the time to learn and apply these concepts you’ll be firmly set on the path to success.
Remember, design is always evolving. Look at what other people are doing and think about how you can apply their techniques to your own work: it’s a great way to hone your design skills.
Now, all that’s left is to put your creative cap on and create your own work of art. Happy creating!
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
17 Best FREE Web Hosting Services
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

Is free website hosting any good? Well, “free” is always good but not always worth it in the long run. Let me explain:
In short, if you want to run a test website, you’re not expecting to get much from it, and you don’t want to invest any money into it at all, then free website hosting might indeed work for you!
In 95% of other cases, you’re going to be better off with a cheap website hosting plan like Bluehot, Hostinger etc. no more expensive than $2.75 or even $1.99 per month (small businesses or online stores often choose something in this price range).
If you’re in a hurry, here’s a summary of our findings based on the analysis below:
Free website hosting is okay for a hobby project or a proof-of-concept type of project. It’s okay if you want to run a site for a short while, get your data and then shut it off.
For any sort of serious website building project or a site that’s meant to stay online for a long while, you’re better off with an affordable web hosting plan or even a pick from the very best web hosting services out there.
For example, Bluehost is our recommended self-hosted website server. If you check them out through our link, you’ll unlock a special discounted price of $2.75 / mo vs the $3.75 standard entry-level price. You also get a free domain name bundled in.
Alternatively, you might opt for an all-in-one solution. For example, Wix is a good choice for a quick start, covering both hosting and website builder in one place. Although there is a free plan, you can try any premium plan offering 14 days of money-back.
Want to get the full story? We compared 17 best free website hosting options to help you make your decision.
The limitations of free website hosting
In life, you tend to get what you pay for, and web hosting is no exception. If you choose the free hosting route, be prepared for some common issues that come along with it.
Even the best free hosting tends to be fairly unstable, which can result in downtime. Also, providers typically place restrictions on storage space and bandwidth, limiting your site’s growth and traffic capacity. Your personal website or business website may also have slow performance.
That said, there are times you may want to consider free hosting. For a personal project, it may be all you need. The same is true if you’re practicing your web design and web development skills and just want a space to try out new ideas.
Perhaps you’re setting up an area to test new plugins or themes. In that case, the limitations of free hosting shouldn’t be a barrier to what you want to accomplish. Of course, if you simply need a staging site, you may want to use a local development tool, such as Local, and not worry about hosting at all.
However, if you need a live site and don’t want to deal with the drawbacks of free web hosting, there are some affordable alternatives to consider. A cheap host can help you keep your budget low while avoiding poor site availability.
17 Best FREE Website Hosting Services
The good news is that you can test drive free website hosting at no cost to see if it might work for you. If you’ve decided to give it a try, here are 17 options to consider.
1. InfinityFree
InfinityFree is a free web hosting service that boasts a 99.9% uptime guarantee. It offers users:
- An auto-installer with more than 400 different apps, including WordPress
- Free subdomains
- 5 GB disk space
- Unlimited bandwidth
- 400 MySQL databases
- Knowledge base support
You’ll also have access to the Softaculous Script Installer to set up WordPress. This hosting service provider doesn’t offer domain registration, but you can use one you’ve acquired from another registrar.
Once your website is published, your visitors won’t see ads. However, there will be ads in cPanel on the back end. Your site is also limited to 50,000 hits per day.
2. Wix
Wix is a drag-and-drop website builder – similar to tools like Weebly or Squarespace; and yup, you don’t need to be familiar with PHP, like you do with other solutions (e.g. – Joomla).
However, we’re featuring Wix on this list because it’s kind of an all-in-one solution for both a website platform and server space to host that website. Since Wix does come with a free plan, this makes it a free website hosting service as well. This free website builder is a unique way to enjoy awesome site-building features backed by enterprise-grade reliability. On that free plan, you get:
- Wix.com subdomain
- Beautiful templates
- 500 MB disk space
- 500 MB bandwidth
- Global content delivery network
- Free SSL and security monitoring
- Knowledge base and customer support
- Decent load times
Unfortunately, if you’re expecting no ads, you will be disappointed. Just like most of the free web hosting providers, Wix places their own ads on free plan sites. You can only connect a Wix subdomain and would have to move to a paid plan for connecting a custom domain.
The eCommerce functionality is also unavailable in the free version. However, you can still set up things like bookings, events, and forums, and fill in your site with SEO-friendly content with just a few clicks.
3. ByetHost
ByetHost is another free hosting service that you could use. Its plan features:
- Five subdomains
- 1 GB disk space
- 50 GB monthly transfers
- One MySQL database
- 24/7 support via ticket system and knowledge base
ByetHost offers solid support for its free plan, which can be rare. You can access a self-service knowledge base and video tutorials, but a ticketing system is also available.
In addition, you’ll receive usage statistics such as disk space, bandwidth usage, and daily hits. You can find this data in VistaPanel, which is ByetHost’s free hosting control panel. Then, you can use the information to help budget your resources.
4. 000WebHost
000WebHost is a free hosting option from Hostinger. Some of its features include:
- One website
- 300 MB disk space
- 3 GB of bandwidth
- One MySQL database
- Community forum
000WebHost comes with the Zyro website builder, which should make designing your site less intimidating. Like InfinityFree, visitors to your website won’t see ads, but there will be ads in your WordPress dashboard.
Free hosting from 000WebHost doesn’t even require a credit card to set up, and you can use it as long as you like. Also, if you outgrow your free plan, you can easily upgrade to a cheap plan from Hostinger. Hostinger plans start at $1.99 / month for your first billing cycle.
5. Google Cloud Hosting
Google Cloud Hosting isn’t technically free. However, it does offer a one-year free trial that includes:
- One website
- Unlimited storage
- Extensive support documentation
While Google Cloud Hosting is tailored towards large businesses, anyone can use it. To get started, all you need is a Google account.
The free trial lasts for 12 months, or until you’ve used up the $300 credit it includes. After this, you only pay for the resources you use. Google offers a price calculator to help you estimate your costs.
6. AwardSpace
AwardSpace offers a variety of hosting services. It’s best known for its free plan, which includes:
- One website
- Three subdomains
- 1 GB disk space
- 5 GB bandwidth
- MySQL database
- 24/7 live chat
Awardspace includes one-click content management system (CMS) installation as well as the Zacky website builder. Also, the 24/7 live chat is available to free plan users if you have questions.
Once launched, your own website will be ad-free. Plus, you can place ads to monetize it. AwardSpace provides you with the ability to monitor your bandwidth usage as well, which may help you budget your resources.
7. Freehostia
Freehostia offers paid and free hosting. The free plan, called ‘Chocolate’, provides:
- Five websites
- 250 MB disk space
- 6 GB bandwidth
- One MySQL database
- FAQ and ticket support system
Freehostia’s cluster platform aims to offer more reliability from its free hosting. Hopefully, this results in less downtime for your website.
You’ll have access to a website builder complete with templates. If you run into issues, you can have an answer to your support ticket in one hour, even with the free plan.
8. FreeWebHostingArea
FreeWebHostingArea is a volunteer-maintained free hosting service. It offers:
- 1.5 GB disk space
- Unmetered traffic
- MySQL databases
- Free email support
9. W3Schools Spaces
W3Schools Spaces features of the free plan:
- Free templates
- Allow 500 requests/month
- Allow 100MB data and storage/month
- Free SSL
10. Glitch
Glitch features of the free plan:
- Provide 4000 requests/hour
- The server processes 512MN of RAM
- Storage capacity 512MB
- Unlimited static sites
- Support import/export Github function.
11. Fleek
Fleek features of the free plan:
- Support to edit domains
- Provide services https
- 3GB of storage
- Unlimited websites
- Automatically deploy on Git
- 250 minutes to build and 50GB of bandwidth
- Free SSL
12. Netlify
Netlify features of the free plan:
- Automatically built from Git
- Deployed on the global edge network
- Bandwidth: 100GB/Month
- Number of websites: Unlimited
- Restorable to any version
- Provides a free CLI.
13. Render
Render features of the free plan:
- 100GB/month for bandwidth and storage
- Lightning-fast CDN
- Can custom domain with full SSL functionality
- Automatically deploy on Git
14. Surge
Surge features of the free plan:
- Provides 404.html page functionality
- Unlimited websites and APIs
- Can custom domain
- Easy to deploy via CLI
- Unlimited websites.
15. Vercel
Vercel features of the free plan:
- Improve website performance with Edge Network
- Unlimited websites and APIs
- Can custom domain with full SSL functionality
- Provides Serverless Functions
- 100GB bandwidth/month
- Automatically optimize images (1000 images for the free version)
16. Firebase
Firebase features of the free plan:
- 10 GB of storage
- 360MB Bandwidth/day
- You can edit your website’s domain name
- Allows multiple pages to be added to the same project
- SSL support.
17. HyperPHP
HyperPHP is a free hosting and domain service for personal websites. Its plan offers:
- 1 GB disk space
- Free subdomains
- MySQL database
- Free tech support and community forums
HyperPHP offers a few ways to make launching a new website easy. Firstly, a free domain transfer is available. This host also offers an automatic script installer, which you can access through VistaPanel.
FAQs - Free Web Hosting
1. Is free web hosting reliable?
Answer : No, free web hosting isn’t reliable. Most free web hosting has absurdly limited resources and you’re also likely to run into multiple issues. This includes poor performance, complicated interface, compromised security, and ads on your website. Not to mention questionable terms of service.
2. Can I get free hosting and a domain?
Answer : Free hosting and domain is rarely possible, none of the providers here has such a deal. However, many hosts offer free subdomain hosting. You can choose a desired name for your site, but it will look something like this: desiredname.freehosting.com.
3. Can I use free hosting for selling online?
Answer : Yes, as long as you can host WordPress and install WooCommerce on your paid plan, it's possible to sell online using free hosting. Yet, it’s extremely likely to cause many problems and potentially ruin the seller/buyer relationship. If your online store is always down or very slow, the buyers will simply go to more professional sites.
4. Can I host my own website?
Answer : Yes, you can host your own website if you have the tech skills and 100% uninterrupted network. It will require significant skills, technical know-how, resources, and time among other things. Plus, many Internet service providers also forbid personal hosting.
5. Does it matter where you host your website?
Answer : Yes. With a bad hosting provider, your website may be plagued with slow loading times, a lack of proper security, and extensive downtime. It’s really important to choose a web host with a discerning eye.
Conclusion
While your free web hosting platform might not be perfect, it can be a viable option in some scenarios. However, finding a quality provider that delivers on its promises is no easy task.
In this article, we shared our opinions on the 17 best free website hosting options available. You have nothing to lose by giving one a try. Our top pick in the category of best free web hosting is AwardSpace for its 24/7 live chat support and easy WordPress installation.
However, for any type of serious project, we recommend using at least a cheap paid shared hosting service. In our collection of cheap web hosting sites, you’ll find services that cost just a few dollars per month.
As we mentioned earlier in this post, you can get quality, affordable website hosting like Bluehot, Hostinger etc. for $2.75 or even $1.99 per month
Recommendation - Paid Web Hosting Service Providers
If you are looking for safe and secure website hosting, we recommend to use paid web hosting services.
Read More : You can explore here 30+ Best Web Hosting Providers 2023
Video - Best Web Hosting For Small Business
Affordable Website Hosting for your domainIf you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Unlocking Success: How Web Design and Development Impact Your Online Presence
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

In the era of rapid digital advancements, establishing a formidable online footprint becomes imperative for the triumph of any business venture. A meticulously crafted and expertly engineered website can potentially wield a profound impact on the perception of your brand, ultimately ushering you toward the gateway of triumph. Within the confines of this article, we shall delve deep into the realm of web design and development, unraveling its intrinsic capabilities to instill a positive transformation in your virtual presence. Brace yourself as we commence this enthralling odyssey toward attaining boundless success!
The Power of First Impressions
In the realm of your website, initial impressions hold immense significance. Studies have revealed that mere seconds are all visitors take to shape their perception of your site. Hence, it becomes paramount to fashion a design that is visually enchanting and user-friendly, seizing your audience's attention right from the moment they land on your virtual domain.
An aesthetically captivating framework, complemented by alluring imagery and captivating content, possesses the power to leave an indelible mark on your visitors. It conveys a sense of professionalism, credibility, and reliability, all of which are pivotal elements in establishing a robust online presence.
Navigating the User Experience
The success of a website is intricately tied to the user experience (UX) it offers. The seamless flow of navigation, an intuitive interface, and flawless functionality collectively contribute to a positive user experience. It is imperative that visitors can effortlessly find the information they seek, devoid of any sense of confusion or frustration.
The user experience can be considerably improved by adding simple navigation menus, clear call-to-action buttons, and strategically arranged content. By placing utmost importance on user experience during web design and development, you can effectively captivate and retain your audience, minimize bounce rates, and maximize conversions.
Mobile Optimization: A Must-Have
In an era dominated by the ubiquity of smartphones and tablets, optimizing your website for mobile devices is not merely a choice—it has become an absolute necessity. Neglecting the necessity of mobile optimization can seriously harm your online presence because a substantial amount of internet traffic comes from mobile users.
Responsive web design ensures the seamless adaptation of your website to diverse screen sizes and resolutions. It guarantees a consistent and intuitive user experience across a myriad of devices, thereby empowering mobile users to navigate and engage with your digital domain effortlessly. By embracing the essence of mobile optimization, you can extend your reach to a broader audience while concurrently enhancing your search engine rankings.
Leveraging Social Media Integration
Social media has become an inseparable part of our daily lives in our modern interconnected world. Harnessing the power of social media integration in your web design and development endeavors can revolutionize your online presence.
By seamlessly integrating social sharing buttons on your website, you can actively encourage and empower visitors to effortlessly share your valuable content with their extensive networks. Furthermore, real-time social media feeds display allows you to showcase captivating updates and actively engage with your cherished audience. By forging a solid and seamless connection between your website and various social media platforms, you can expand your reach, nurture unwavering brand loyalty, and attract a fresh influx of new followers.
Consider using QR codes as a cutting-edge and creative strategy as well. By strategically incorporating QR codes into your web design, you can provide a quick and convenient way for users to access and share your website or specific content. QR codes act as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds, enabling effortless interaction and expanding the potential for connection with your target audience.
Search Engine Friendliness: Climbing the Ranks
Unleashing triumphant outcomes within the digital landscape necessitates a profound grasp of the indispensability of search engine optimization (SEO). A meticulously optimized website can heighten your visibility in search engine results, propelling organic traffic and magnetizing prospective clientele.
To augment the search engine friendliness of your website, integrate pertinent keywords seamlessly into your content, meta tags, and headings. Skillfully employ appropriate HTML tags, such as H1, H2, and H3, to meticulously structure your content, thereby endowing search engines with a clear comprehension of your website's hierarchical framework. Additionally, craft descriptive and succinct meta descriptions for each page, enthralling users and enticing them to click through to your digital abode fervently. By meticulously implementing these SEO strategies, you can fortify your online presence and unlock the gates to unrivaled success.
Enhancing Loading Speed: Faster Than a Blink
In the contemporary whirlwind of our world, swiftness reigns supreme. Research unequivocally demonstrates that users demand websites to load swiftly within two seconds or less. Any semblance of delay in loading speed can elicit exasperation, urging visitors to forsake your digital abode in favor of a nimbler alternative.
Optimizing your website's loading speed is an imperative measure to avert the potential loss of visitors. Embrace techniques such as image compression, minimizing HTTP requests, and harnessing caching mechanisms, as they wield power to enhance loading times significantly. By according to the importance to speed within your web design and development endeavors, you can seamlessly bestow a browsing experience without hindrance, thereby ensuring the unwavering engagement of your cherished users.
Maximizing Accessibility for All
Web accessibility is a paramount facet of web design and development that must never be disregarded. Ensuring the accessibility of your website to individuals with disabilities resonates not only as an ethical imperative but also as a legal mandate in numerous jurisdictions.
Incorporate proper HTML tags, furnish an alternative text for images, and employ descriptive link texts to facilitate users utilizing screen readers. Deliberate upon color contrast to enhance readability and extend keyboard navigation options to cater to those unable to hire a mouse. By rendering your website accessible to all, you exhibit an unwavering commitment to inclusivity, fostering a positive online presence that reverberates with the utmost integrity.
Conclusion
Realizing unprecedented triumph within the digital realm necessitates acknowledging the profound influence of web design and development on your online presence. According to the paramount importance of factors such as visual allure, user experience, mobile optimization, search engine friendliness, and accessibility, you pave the way for creating a captivating website that magnetizes and enthralls your intended audience. Remember, your website serves as the digital countenance of your brand, and investing in its design and development catalyzes your unparalleled accomplishments in the online sphere.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
Optimizing Web Design for Slow Connections
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech

In today's digital landscape, high-speed internet is commonly expected to work efficiently. However, designing websites for users with slow internet connections is a critical yet frequently overlooked aspect of web development.
Slow internet speeds can significantly impact user experience. They can lead to frustration and an increased bounce rate. Optimizing web design for these users increases accessibility. This upgrade not only benefits users but also boosts engagement across all demographics.
1. Understanding the Challenge
To properly optimize for slow connections, it is critical to understand what issues the user encounters. Many people, particularly those in rural or underdeveloped areas, experience unstable internet speeds. This causes longer loading times. Even the slightest decline in page load times can significantly decline conversion rates and customer satisfaction. Addressing these concerns necessitates a deliberate strategy that focuses on speed and efficiency without compromising the design quality. Bizango provides outstanding web design services to boost lead generation and enhance customer experience.
2. Strategies for Optimization
Here are some strategies you should consider implementing:
- Optimized image and media delivery: Images and media assets dramatically affect website load speeds. Image compression, lazy loading, and responsive image delivery can all help to minimize file sizes and speed up a website's loading time. By prioritizing important content and deferring non-essential elements, websites can provide a faster experience while ensuring a visually engaging presentation.
- Minimizing HTTP requests: every element on a webpage necessitates an HTTP request. This can also lead to a poor loading time. To reduce these requests, consider consolidating CSS and JavaScript files. You can also reduce the utilization of third-party plugins. Using browser caching to store frequently accessed resources locally can also be helpful.
- Simplified design principles: Consider adopting a minimalist design strategy to increase aesthetic appeal while improving performance on slower connections. Focus on the essential elements and streamline navigation. Also, reduce any unnecessary animation and complex interactions. This strategy ensures that users have quick access to vital information.
3. Designing for performance
Implement gradual enhancement tactics. Provide a basic, usable experience to users with weak connections. Begin with a lightweight, text-based interface, which helps load a page faster. Progressively enhance the experience with images, videos, and interactive elements for people with faster connections. This technique ensures that everyone has a satisfactory experience.
Mobile devices often rely on slower network connections than PCs. A mobile-first design encourages designers to prioritize performance and efficiency on smaller screens and slower networks, promoting a more inclusive web experience.
4. Testing and Optimization
Use tools like page speed insights, webpage tests, or lighthouses to access data on loading times, resource efficiency, and overall performance metrics. These tools offer practical insights into areas that require optimization. Make sure to check and ensure that the website runs optimally on all devices and at all connection speeds.
Solicit user feedback, particularly from individuals with slower connections to access the website. Analyze user behavior using analytics solutions to understand surfing habits better.
Endnote
Optimizing web design for slow connections is more than just accommodating a small group of people. It is also about promoting inclusivity and improving the overall user experience. Web designers may design user-friendly and engaging websites at various internet speeds. They can establish this through tactics such as effective media distribution and streamlined design concepts. Prioritizing performance benefits all by increasing user retention rates and the website's overall success.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.
What to Do if Your Website Has Had Problems
Last updated on January 19, 2025 by RGB Web Tech
Your website having problems is not necessarily your fault, and yet, you have to deal with it anyway. Although many websites run into problems at some point or another, this can affect your reputation and your customers’ trust. This means that you need to solve the problems and do better for the future ASAP. Then, here are a number of steps that you can take if your website has had problems, whether they are your fault or not.
1. Work Out the Problem
A huge number of business websites fail. There is no point in trying to solve something that you do not know the details of. Rather than stabbing in the dark and hoping for the best, you should spend some time trying to isolate the problem that has started to affect your website- and your business. For instance, you need to establish whether it is an issue with your hosting provider, with an add-on, or with your cybersecurity measures. Once you have done this, you will have a better idea of the solution and what you need to do to get your business back up and running online again.
2. Tell Your Customers About the Problem
The next step that you should take is to inform your customers of the issue. Although it can be tempting to hide it and hope that they do not notice, this can have a negative knock-on effect and can prevent customers from trusting or ever coming back to your business. The more transparent you are, the better. Not only should you inform customers of the problem with your website, but you should try to make it up to them, especially in the case of limited-time sales. For instance, you might offer a discount or extend a sale period.
3. Start from Scratch with Your Website
Sometimes, your website will be unfixable, or the way that it is structured means that problems will continue to crop up. If this is the case, you might decide to start from scratch to create a great website. To do this, you should search for a new website hosting system and provider, and look for website builders that can give you the themes that you need to create a website in a few clicks of a button. Although changing your domain name can be hard on your business and its customer base, by keeping them informed every step of the way and linking this to your social media profile, you should be able to make the transition a success.
4. Get a Professional Designer Involved
A professional designer can help you to get back on track when it comes to your website, especially if you have not used them before. A professional designer will be able to create a navigable and accessible website that suits everyone. Their designs will be flashy and exciting, while directing customers to the information that they need. Their designs should also be functional, without any broken links or other issues, and this can help you to impress your customers rather than frustrate them. It can also allow you to boost your Google ranking position.
5. Look for Cybersecurity Solutions
If the issue was a cybersecurity matter, and this has had a financial and reputational impact on your company, there is only one action to take: opt for an improved cybersecurity solution. There are many systems out there to help you, and, in most cases, it is not enough to simply choose one. This means that you should look around for a firewall, encryption software, and Cloud security that can benefit your website in the long run. You might also check out identity threat detection if this was the source of your problems.
6. Get Your Business Back Up and Running
However, your most important short-term goal should be simply getting your business back up and running. The longer you are offline, the more business you will lose, and many small companies cannot afford to lose even a day’s worth of business. This means that you should work around the clock to save your company and look for temporary alternative solutions that can keep your company going. For instance, you might find a different selling platform, or you might seek to reinvest more into your physical marketing and brick-and-mortar efforts, if you have them. This will ensure that there is not a dip in profits or interest, which your competitors can ultimately take advantage of. Once your business is gone, it is unlikely to come back, even once you have rescued your website.
If you found this article helpful, we encourage you to share it on your social media platforms—because sharing is caring! For more information about article submissions on our website, feel free to reach out to us via email.
Send an emailWritten by RGB Web Tech
Latest Technology Trends
Latest technology trends shaping the future, including AI advancements, blockchain innovation, 5G connectivity, IoT integration, and sustainable tech solutions. Explore breakthroughs in quantum computing, cybersecurity, augmented reality, and edge computing. Stay ahead with insights into transformative technologies driving innovation across industries and revolutionizing how we live, work, and connect.





